Actinic Keratosis
Actinic Keratosis (AK) refers to a scaly spot formed on the sun-damaged skin. It is also known as solar keratosis. Actinic Keratosis is considered to be a precancerous or early onset of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.
Actinic Keratosis usually affects people who live in tropical and sub-tropical regions. Individuals also have the following predispositions: defective immune system, fair skin that has a history of sunburns in the past, history of prolonged sun exposure for work or recreation, and other signs of photoaging skin.
Actinic keratosis is the result of abnormal skin development caused by DNA damage as a result of short-wavelength UVB. These spots usually appear due to ageing, sun exposure, predisposing disease(s), certain drugs, or when the immune barrier is poor.
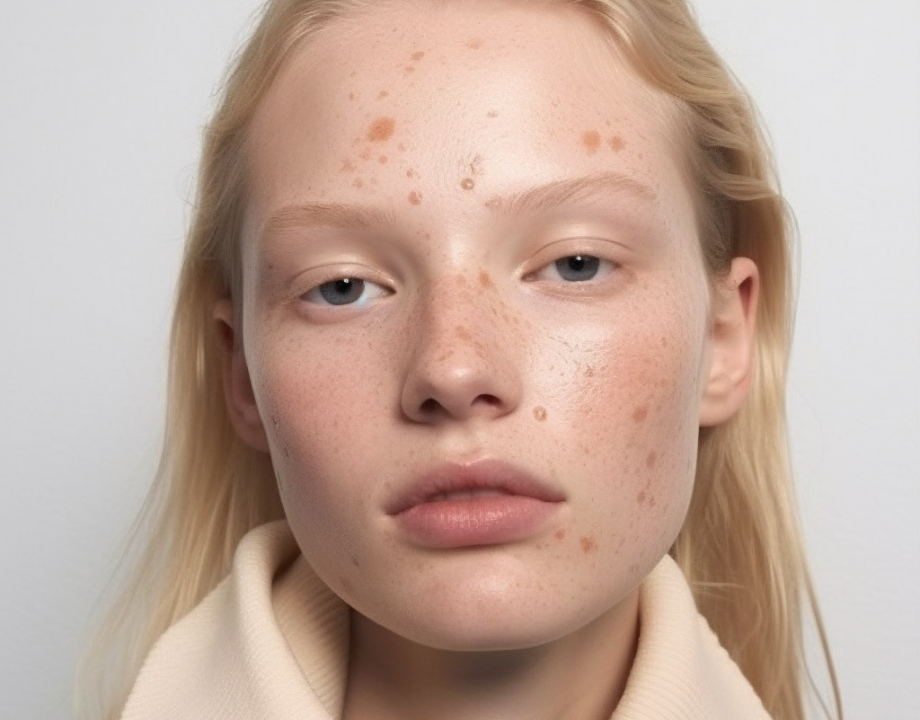
Actinic keratosis has a few distinct clinical features. It appears as a flat or thickened papule or plaque. The surface is usually white or yellow; scaly or warty. The skin is coloured, red, or pigmented.
Actinic keratosis usually appears on sites that are constantly exposed to the sun, which are the back of hands and face. Sometimes, ears, nose, cheeks, upper lips, temples, forehead, and balding scalp can be affected tool. Individuals with severe chronically sun-damaged skin have their upper trunk, upper and lower limbs, and dorsum of feet affected as well.
Actinic keratosis carries certain complications, such as predisposition to the development of squamous cell carcinoma. The solitary actinic keratosis does not evolve to the squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). But the risk of SCC occurring in the patient diagnosed with actinic keratoses is between 10-15%.
The cutaneous horn may be formed from an underlying actinic keratosis or SCC.
Since actinic keratosis is the result of the sun damage, people diagnosed with actinic keratosis are also at risk of developing basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, and rare forms of skin cancer like Merkel cell carcinoma.
Actinic keratosis is usually diagnosed with the clinical assessment that may include dermatoscopy. A biopsy is sometimes required in order to exclude the presence of SCC.
Actinic keratoses are usually removed because they tend to be uncomfortable, but more importantly, there is a risk of developing skin cancer.
The treatment of actinic keratosis involves removal or destruction of the affected skin. The epidermis then regenerates from the neighbouring unaffected follicular keratinocytes.
Actinic keratosis that is found to be tender, ulcerated, thickened, and enlarging has to be treated aggressively.
Physical forms of treatment are used to destroy individual keratoses that appear either in symptomatic form or with a thick hard surface scale.
The spots treatment include cryotherapy or sometimes a surgical option in case of suspicion for skin cancer.
Cryotherapy with liquid nitrogen is the treatment option for treating actinic keratoses. Liquid nitrogen spray is used because it ensures an appropriate depth level and duration of the freeze. Factors like location, width, and location of the lesion determine the depth and duration of freezing. The healing time takes from 5 to 10 days on the face, 3-4 weeks on hands, and more than 6 weeks on legs. A light freeze on the superficial actinic keratosis spot does not leave any mark. However, prolonged freezing time can leave scar or hyperpigmentation.
Shave, electrocautery (burning), and curettage (scraping with a sharp instrument) may be used to remove a hypertrophic actinic keratosis or a cutaneous horn. The wound healing process takes approximately several weeks. After, a specimen is being sent for pathological examination to the lab.
The excision procedure ensures that actinic keratosis is removed completely, which has to be confirmed by pathology. The surgical wound can be left open to heal with the secondary intention or get stitched. The stitches are removed after 7-14 days. The permanent scar will be left from the removed lesion.
In case of extensive areas of the skin affected by the Actinic Keratosis the so-called “field therapy” is used that includes ceratin cream (5-Ftoruracil, Diclofenac, Imiquimod), chemical peels with TCA, and photodynamic therapy.
Actinic keratosis can be prevented by sun protection. If lesions are already present, the condition can be improved by applying high sun protection factor (50+) broad-spectrum sunscreen on a daily basis.
Centre for Medical and Surgical Dermatology offers unique and personalized actinic keratosis treatment options for each patient. For more information on actinic keratosis condition, visit the following link:



4 Comments
Actinic Keratosis – This article is very useful and well researched.
I love this medical blog!
Love your content!
Nice article! Thanks for sharing!