WHAT IS MELASMA?
Melasma is a chronic skin condition which refers to symmetrical, blotchy, and brownish facial pigmentation.
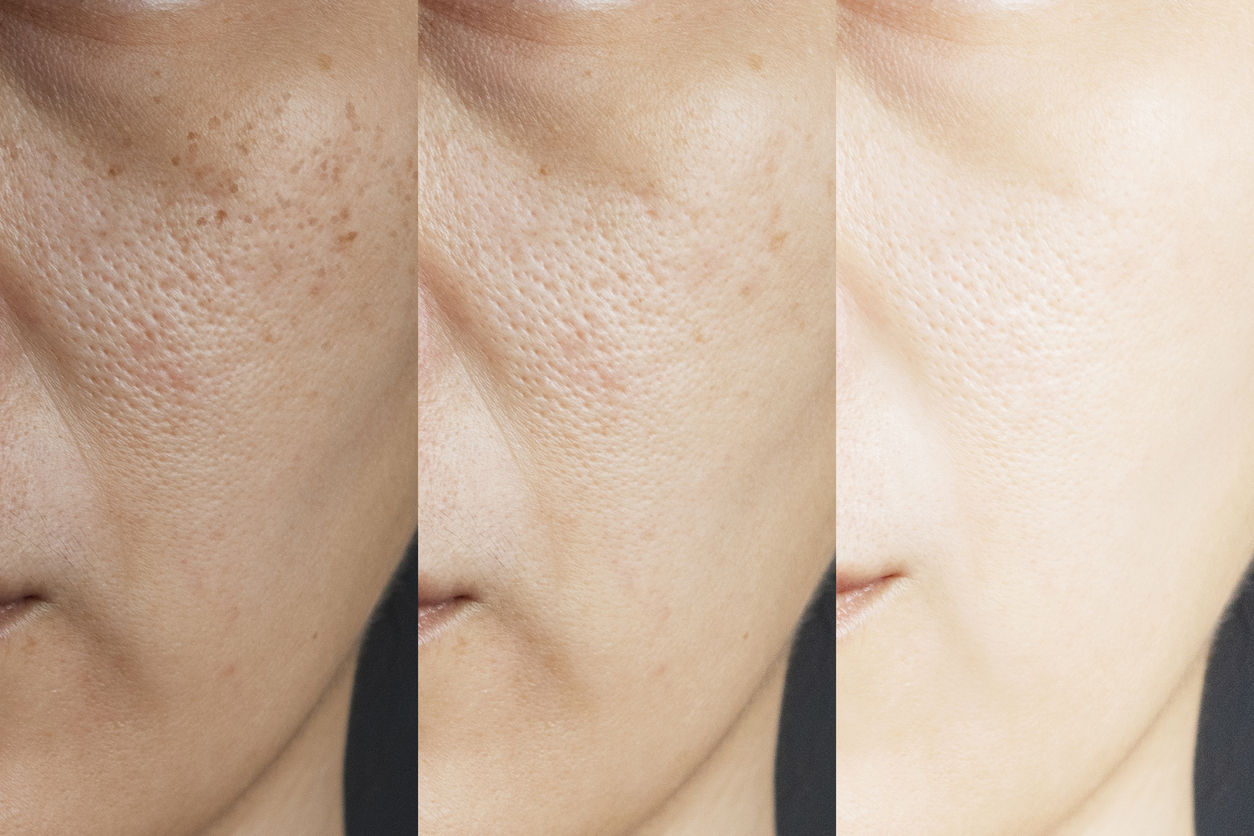
Melasma affects more women than men (only 1 in 4 affected individuals are male patients). On average, this condition appears individuals between 20-40 years old. Individuals with naturally brown skin and those who tan well are in the greater risk in comparison with individuals who have either fair or black skin.
The causes of melasma appear quite complex since multiple factors are involved. Sun exposure and sun damage, pregnancy, hormonal treatments (i.e. oral contraceptive pills), hypothyroidism (low levels of the circulating thyroid hormone), certain products (i.e. cosmetics, scented or deodorant soaps) and medications are all agents that can possibly trigger the occurrence of melasma. Melasma appears in freckle-like spots (macules) and large brown patches on face. These features occur on both sides of the face and spots have an irregular border.
Treatment of melasma condition is quite slow due to the complexity of the condition. Topical therapies are quite common because these medications help to prevent any new pigmentation formation by inhibiting the formation of melanin. The common prescribed options are Hydroquinone 2–4% in the form of cream or lotion; Ascorbic acid (Vitamin C); Methimazole; Azelaic acid in the form of cream, gel, or lotion. Melasma can also be treated with various medical devices, like lasers and intense pulsed light (IPL).
