What is eczema?
Eczema is
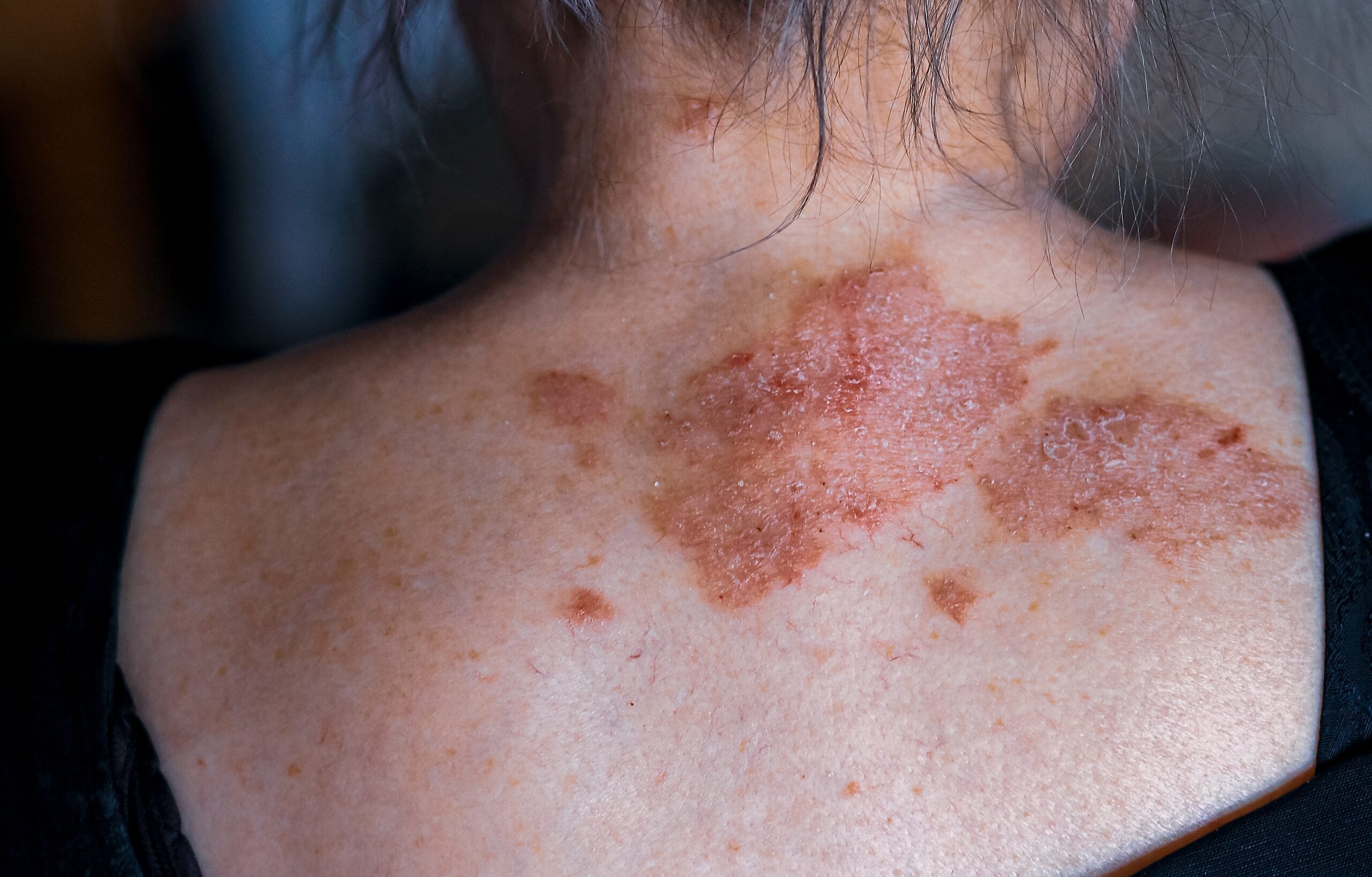
Eczema occurs in phases. There are periods when it peaks and becomes severe. Or there are periods of decline when the condition occurs at the minimal level. Moreover, in some cases, eczema can temporarily disappear from affected areas.
The areas of affected skin and severity of symptoms are unique to each individual and depend on the age. For example, babies with eczema have affected cheeks, arms, legs, back, stomach area, or chest. Meanwhile, children, teenagers, and adults have eczema on the inner part of elbows, back of knees, neck, palms, and soles.
Generally, eczema is triggered by dysregulated immune mechanisms. Patients diagnosed with eczema lack protection from germs in the corneal layer of the skin. The inflammatory response had damaged that layer. Approximately 30-40% of patients have an allergic type of eczema. They usually have more complicated cases of skin inflammation. Besides eczema, they also have either allergic asthma or hay fever. The immune system responses to allergens through the release of antibodies, which in return causes inflammation. Some of the allergens that are potentially linked with eczema are food products (eggs, milk, fish, or nuts), pollen, and dust. However, in most cases, it is impossibles to establish one definitive reason for eczema. Moreover, extreme cold, heat, smoke from cigarettes, and wool can also trigger the disease.
In certain circumstances, dermatitis (eczema) can be caused by the direct impact on the skin of the external allergens causing so-called allergic contact dermatitis. The most common scenarios id the development of dermatitis as an allergic reaction to the metals (nickel, cobalt), baby wipes (methylisothiazolinone), hair colour products (paraphenylenediamine) and many others. In this
Eczema (dermatitis) is diagnosed by a dermatologist through a physical exam. If
Since eczema is a chronic disease, it cannot be completely cured; however, it can be properly maintained. The symptoms of itchiness, redness, and dryness can be regulated by a careful skin care routine and by prescribed medications. Steroid creams may be prescribed because they reduce skin inflammation and itchiness. Besides topical steroids, other classes of medications are widely used, for instance, topical calcineurin inhibitors (tacrolimus, pimecrolimus), and phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor (
Special soaps, cleansers, showers gels, and shampoos will help to maintain the regulation of skin as well. It is also recommended to use moisturizers at least twice a day to prevent the skin from
Besides the usage of various topical products, ultraviolet (UV) light can be also incorporated as part of the treatment. Centre for Medical and Surgical Dermatology also offers treatment of eczema by phototherapy. The UV light helps to block
Systemic medications can be used as an alternative treatment method to topical treatments and phototherapy if the condition of eczema appears to be severe. In medical dermatology, pills and/or injections are considered as types of systemic medications. Antibiotics, mycophenolate mofetil, oral or injectional corticosteroids, azathioprine, small molecules immunosuppressants like methotrexate, ciclosporin, and many more are examples of systemic medications that can be prescribed by a dermatologist to manage severe eczema. Also, there is new biologic medication on the market Dupilumab that is approved for the treatment of severe eczema.
The systemic treatment for eczema should be prescribed only by a board-certified dermatologist who is experienced in managing complex skin conditions. To find a board-certified dermatologist can be done through the service “Find a Dermatologist” of the Canadian Dermatology Association.
One Comment
Comments are closed.
Related Posts


I just like the helpful info you supply on your articles.
I will bookmark your blog and test once more right here frequently.
I’m slightly certain I’ll be told many new stuff right right here!
Good luck for the next!