Treatment of Hives
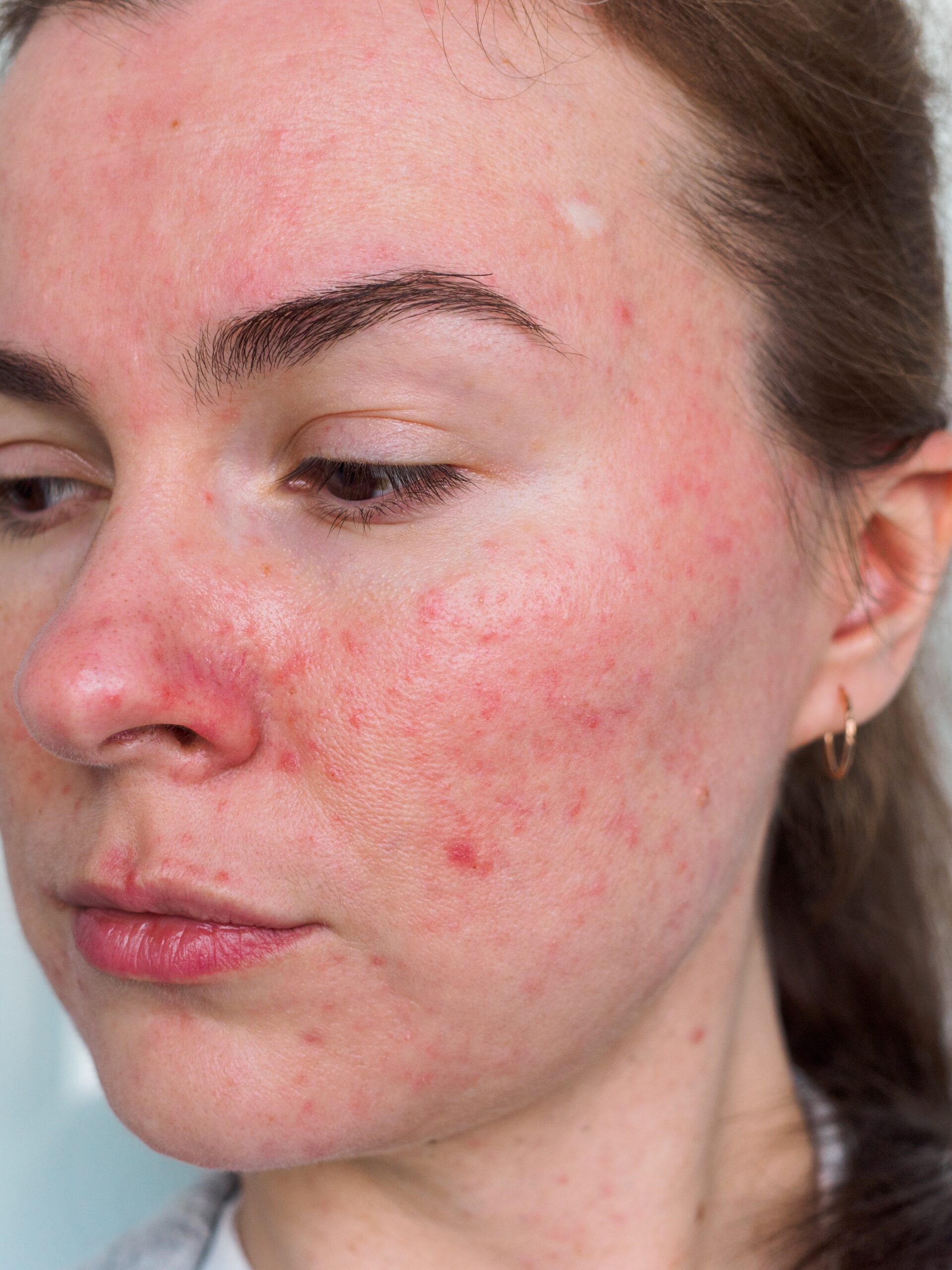
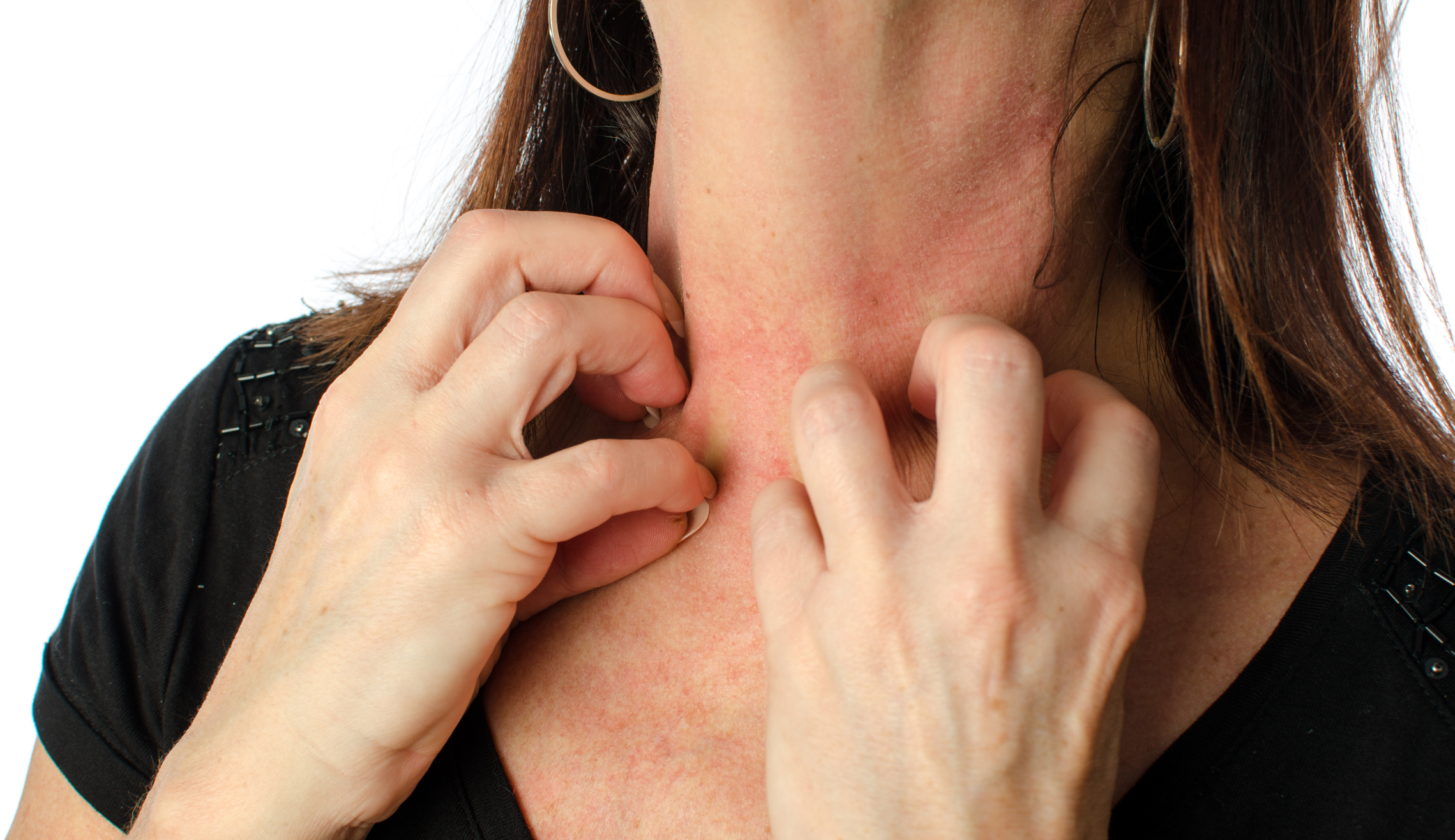
Urticaria (hives) is a medical condition which is characterized by a presence of hives (weals) or angioedema. A weal refers to the skin-coloured or light pink swelling, which is usually surrounded by redness (erythema). The swelling lasts from a few minutes to 24 hours depending on the individual and severity of the case.
The initial treatment for all forms of hives for all age groups is usually done with oral second-generation antihistamines, such as Cetirizine, Rupatadine, Desloratadine, and others in a standard dose. However, if the standard dose is not effective, it can be increased according to the prescribing physician recommendations. The medications have to be taken until urticaria will settle down.
First-generation antihistamines (e.g. chlorpheniramine and promethazine) are no longer recommended for treatment of hives. These medications are short-lasting and have sedative side effects. Moreover, sleep, performance, and learning are reported to be impaired. There have been records of lethal overdoses.
In addition to using antihistamines, the triggering factors of urticaria should be eliminated if known. For instance, potential drugs and/or food allergies should be removed. If relevant type 1 allergens will be eliminated, hives will be cleared out within 48 hours. The affected area is advised to be cooled down with a fan, ice pack, cold flannel, or the soothing moisturizing lotion.
The physical triggering agents are recommended to be minimized as much as possible. For instance, in order to reduce friction, tight clothing should be avoided. For cold urticaria, it is recommended to be dress carefully for cold and/or windy conditions as well as avoiding swimming in cold water(s). For the solar urticaria, it is advised to cover up sun-exposed areas and apply the broad-spectrum sunscreens.
The acute refractory urticaria lasts for less than 6 weeks. Non-sedating antihistamines are usually are the primary treatment options. If they are not effective in the optimized dose, then the short course of oral prednisone or systemic cyclosporine can be used. The intramuscular injection of adrenaline is used only in emergency situations, such as throat swelling.
The chronic urticaria refers to a type of urticaria followed by daily or episodic weals that last for more than 6 weeks. Second-generation oral antihistamines are the primary sources of treatment. If a patient fails to respond to the maximum dosage of second-generation oral antihistamines for 4 weeks then further treatment should be done and the patient has to be referred to the specialist physician- dermatologist, medical allergy specialist or immunologist.
There are new recent advances in the treatment of Urticaria. The new biologic medication Omalizumab showed good evidence in treating patients with urticaria who were resistant to antihistamine medications.
The effectiveness of each treatment can be objectively evaluated through the urticaria control test. Patients have to rate their symptoms over the four week period, quality of life, and overall control of urticaria.
Centre for Medical and Surgical Dermatology offers various treatment options for urticaria which are unique for every patient.
For more information on urticaria condition, visit the following link:
6 Comments
Comments are closed.
Related Posts

Treatment of Hives- definitely an interesting and useful post, especially how often hives can occur.
Thanks for another informative site. The place else may I am getting
that kind of information written in such an ideal manner?
I’ve a undertaking that I’m just now running on, and I’ve been on the look out for such information.
Hello!
Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the great work!
You put so much effort into your blog! Thank you for your hardwork!
Great post! I must say I was impressed how you were able to input all the useful and iporant information into one post. Good Work!
Very valuable information. This blog is exactly what I needed.