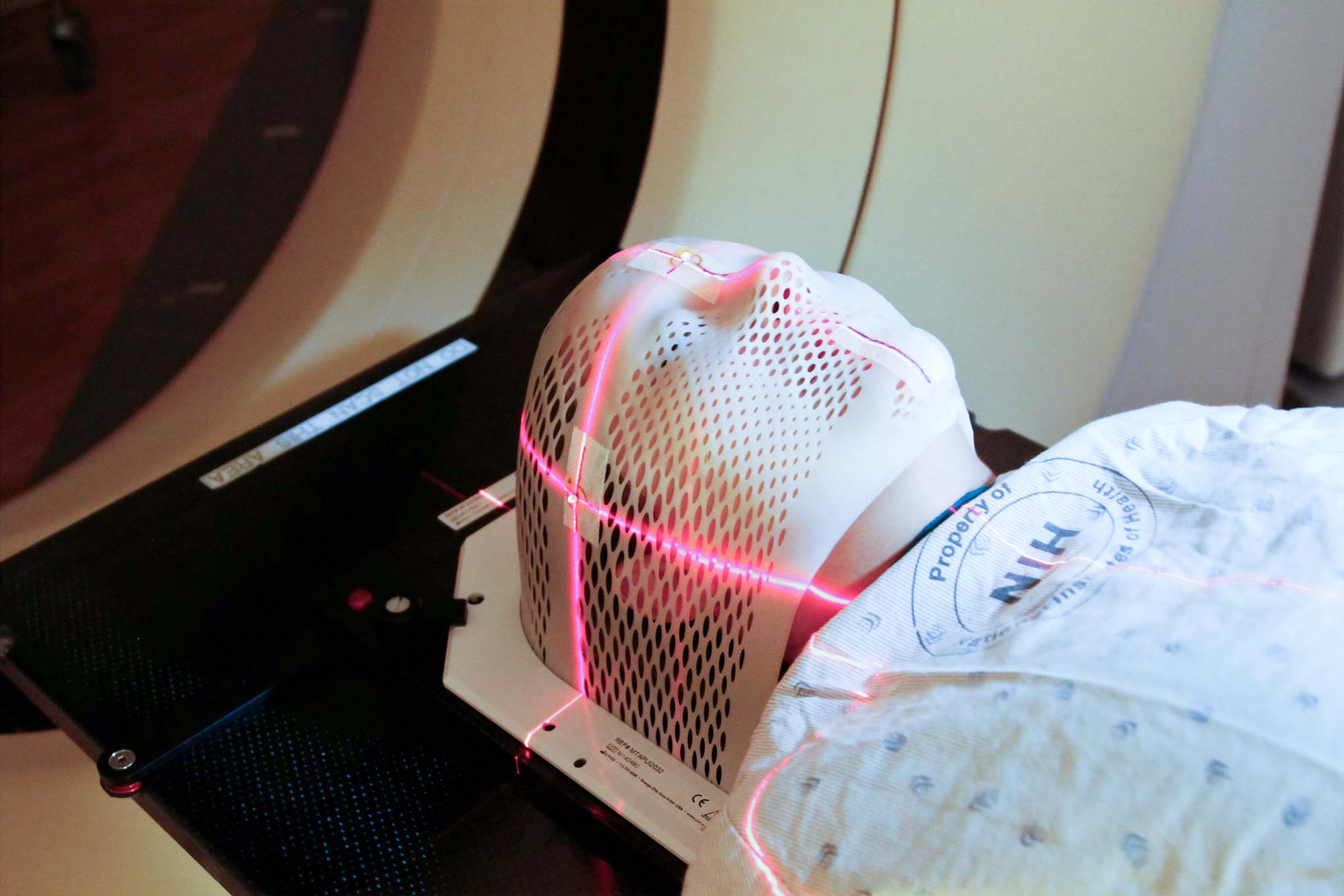
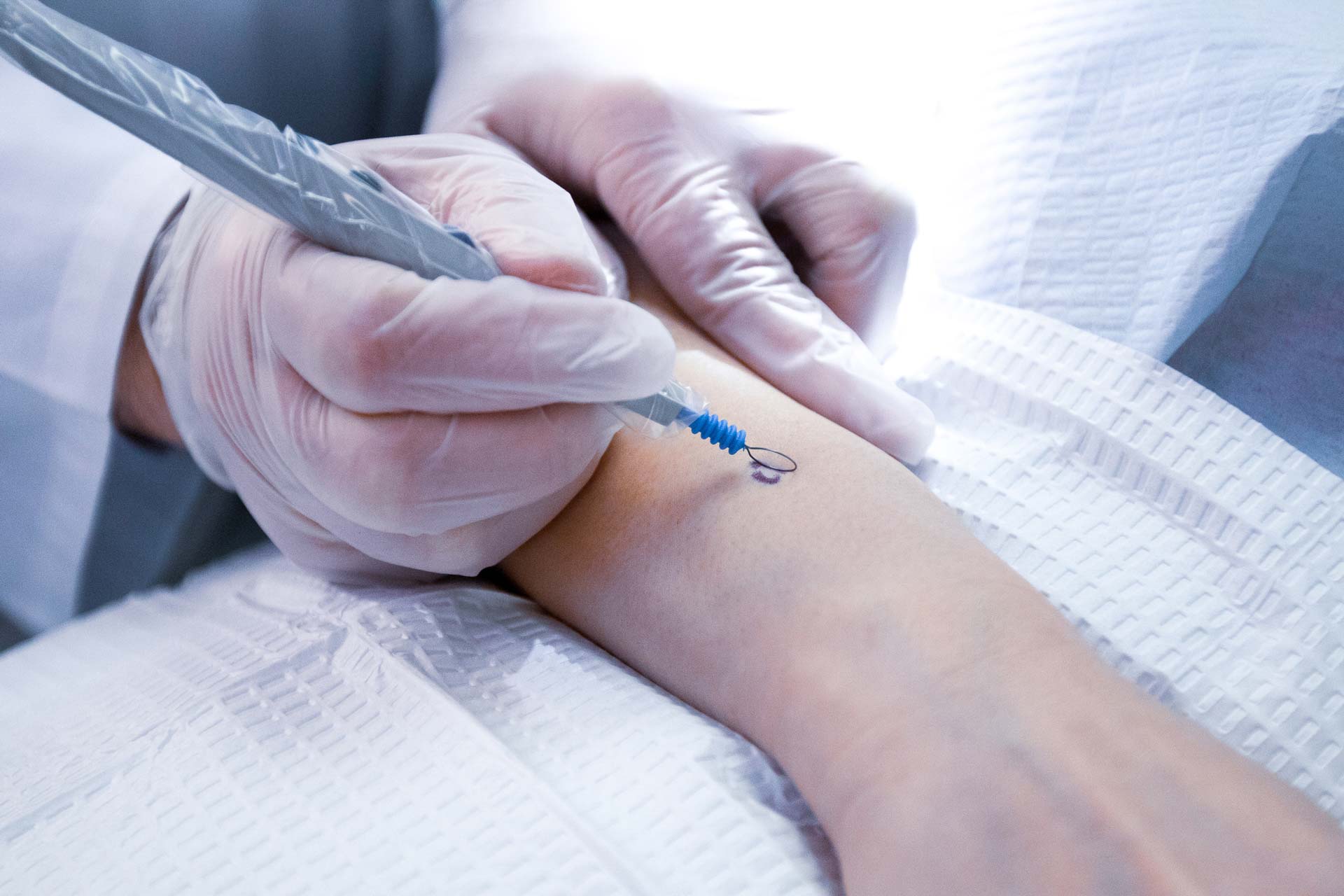
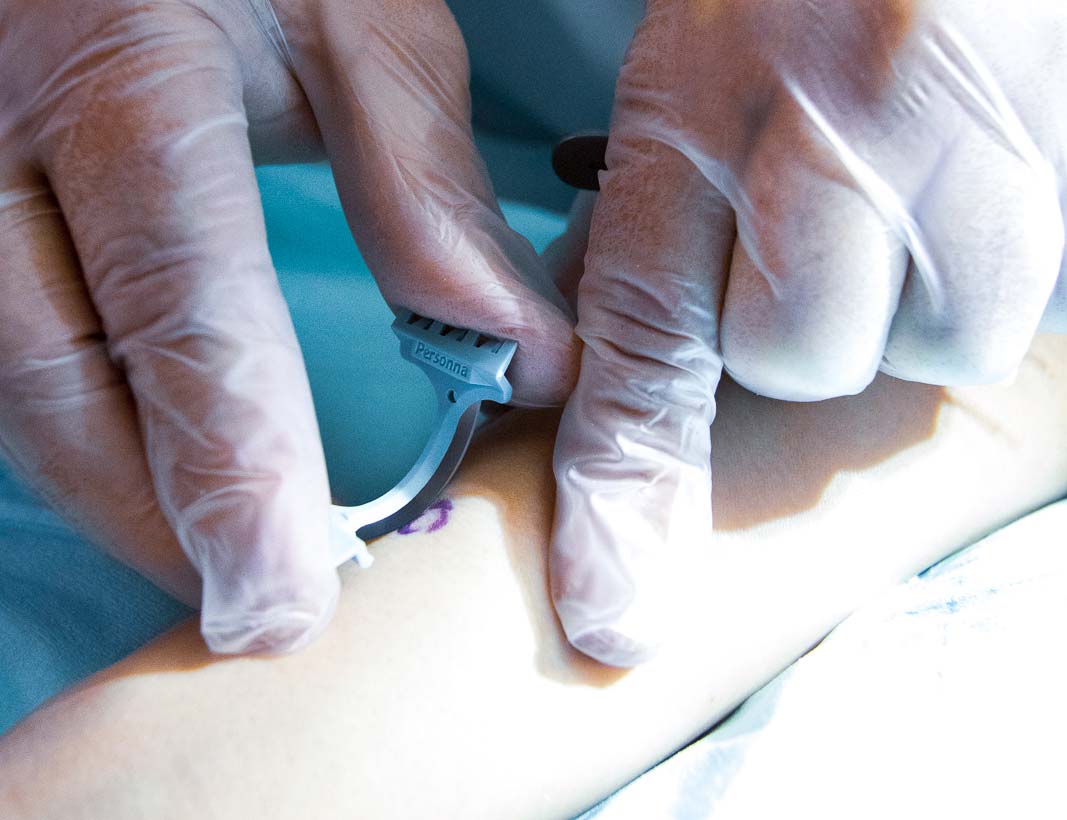
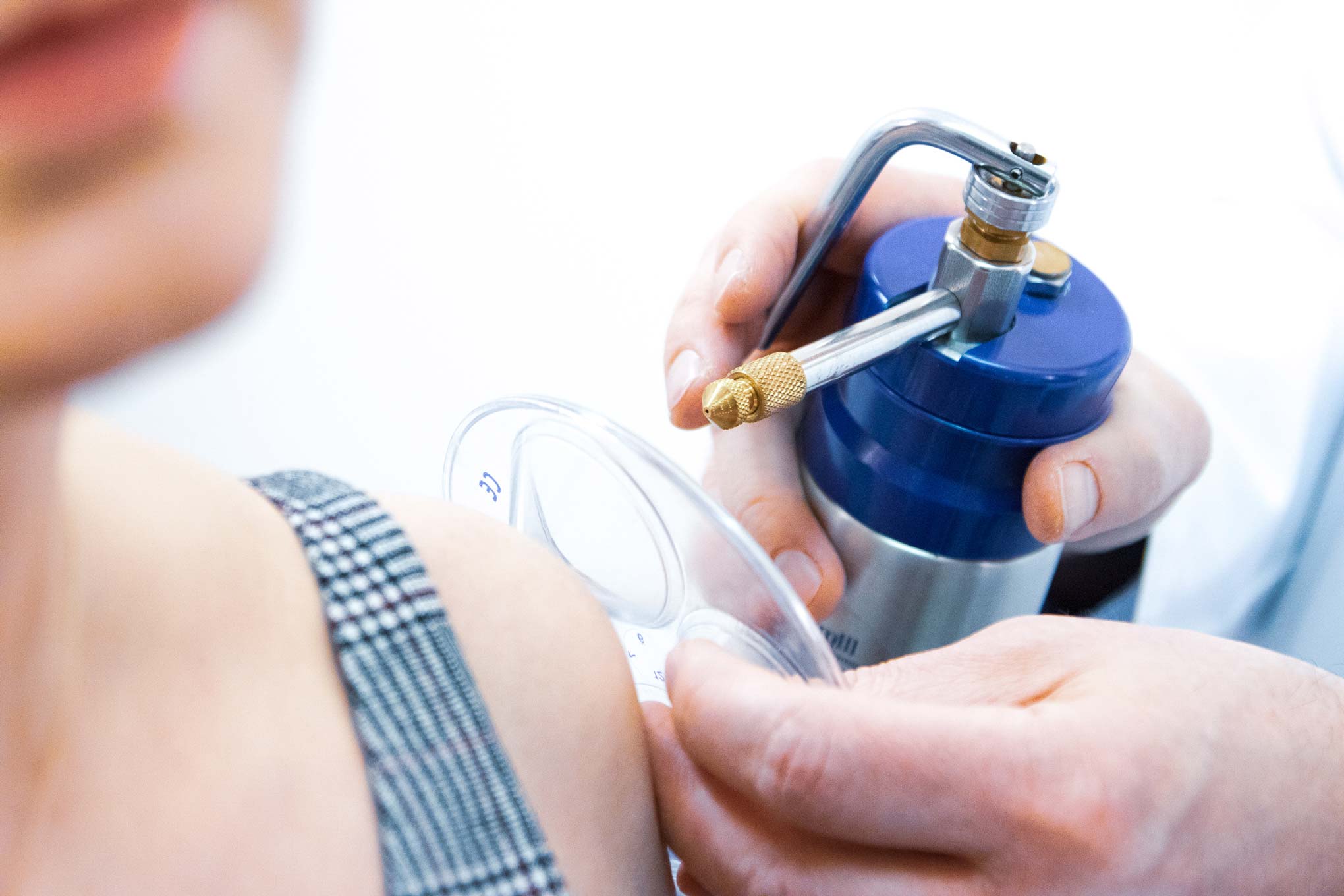
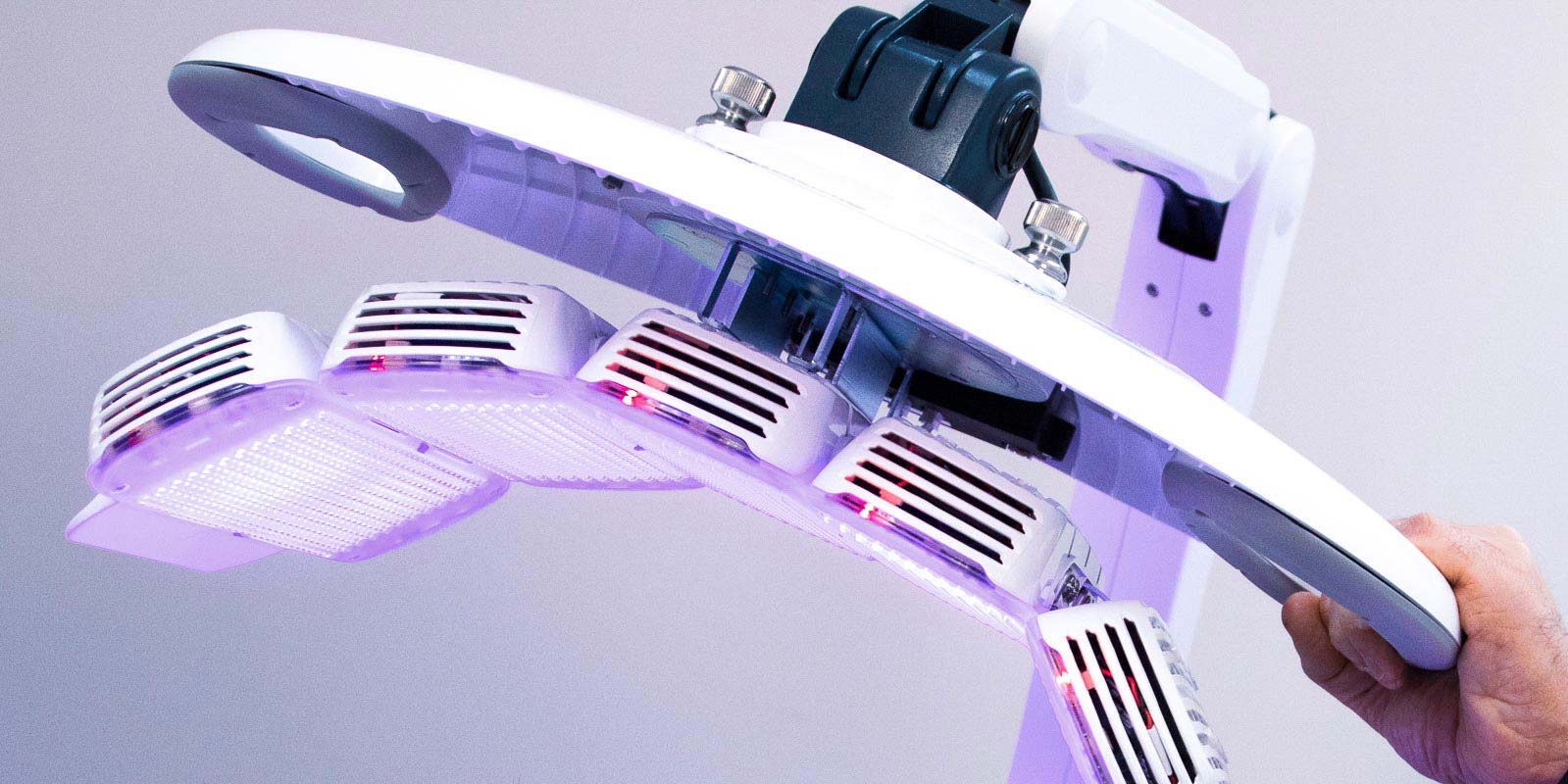
Early detection and expert treatment are crucial for optimal skin cancer outcomes.
Our dermato-oncology services provide comprehensive care for skin cancer patients, from early detection to advanced treatment protocols. We utilize cutting-edge diagnostic technologies and collaborate with multidisciplinary cancer specialists to ensure optimal care.
Each patient receives individualized treatment plans based on the latest medical evidence and international guidelines. Our systematic monitoring and follow-up protocols ensure continuity of care throughout the treatment journey.