Rosin, also known as colophony, is a sticky substance or sap derived from pine and spruce trees. Its sticky form makes it useful in a wide range of different home/recreational and work sources. For example, in home/recreational industries, it is found in adhesives (e.g., glues, tapes), cosmetic products (e.g., lipsticks, eyeshadows, mascaras), toiletries (e.g., hair removing wax and dental floss), chewing gum, paper products, medicines (e.g., cold sore creams, war removers), etc. In work sources, it is found in printing inks, machine belts, veterinary medications, cement, paint, asphalt products, and many more.
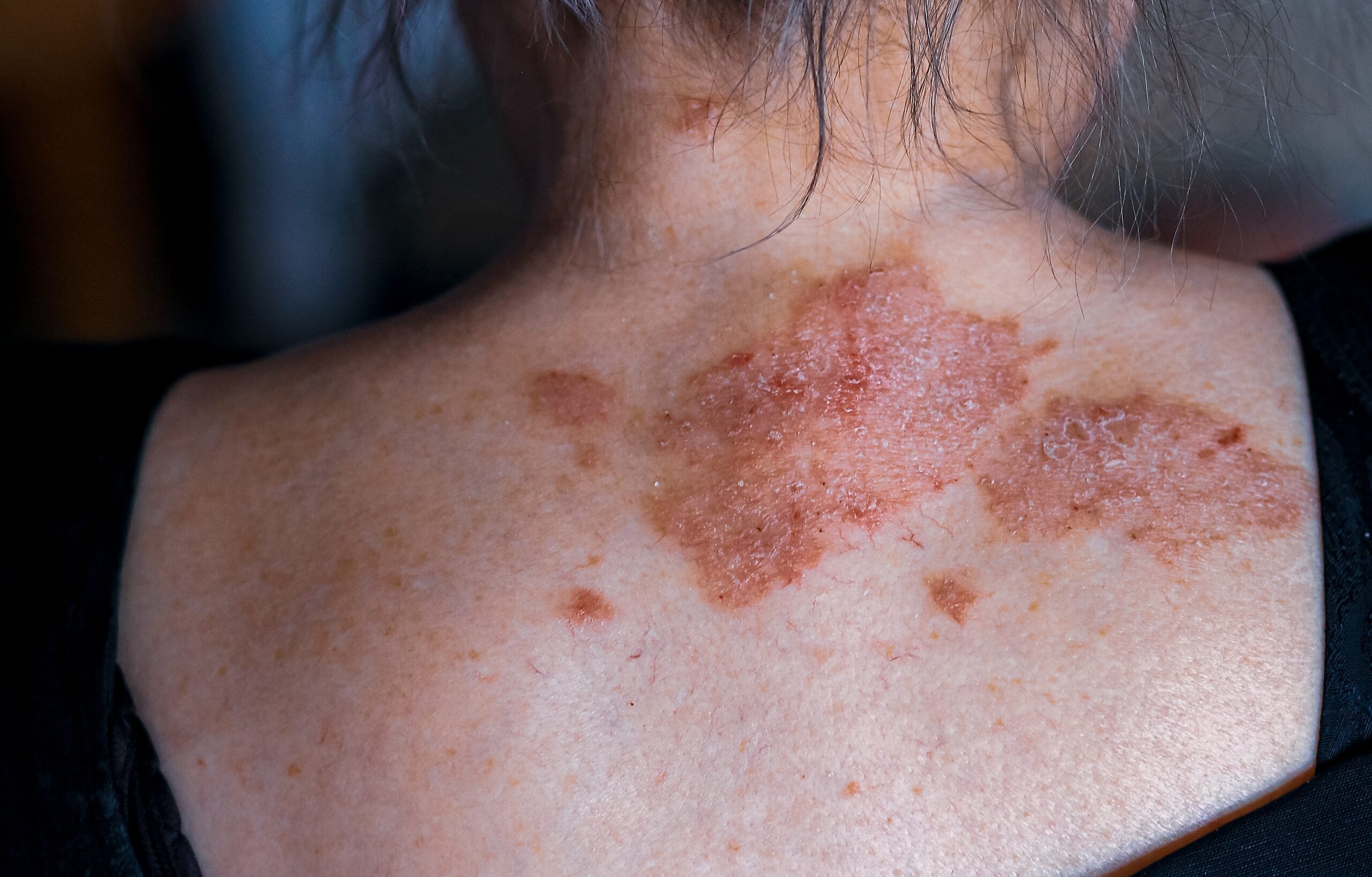
When an allergic individual comes in contact with rosin, their reaction includes experiencing acute allergic contact dermatitis and having difficulty breathing. Allergic contact dermatitis usually occurs after 1-3 days of the initial contact with rosin; however, reactions can occasionally appear within 24 hours or even after the week following the exposure. Dermatitis appears on the site of contact with rosin. For instance, it can appear on the hands and forearms after carrying the pine wood. The initial reaction is red, inflamed, and itchy skin. As the reaction progresses, the skin can blister and become even itchier. If exposure is continued for a prolonged period of time, acute allergic contact dermatitis can become a chronic type with more thickened lichenified skin.
Rosin allergy is diagnosed from the clinical history and by performing patch tests, a special type of allergy skin test.
Avoidance is the only long-term treatment method for rosin allergy. There is no mechanism for de-sensitising to this allergen. Allergic contact dermatitis is treated the same way as any acute dermatitis/eczema by prescribing topical corticosteroids and emollients.
The best way to avoid resin allergy is to be aware of products that contain rosin and are found in one’s environment. It is highly suggested to read through the ingredients on the product labels or packaging of all substances that an individual comes in contact with. Products that do not have lists of all the ingredients should be avoided.
If a product that contains rosin cannot be avoided, it is highly recommended to wear gloves and other protective clothing to avoid contact with the skin. If possible, a material safety data sheet can be requested at the workplace to help identify alternatives that are safe to reduce contact with materials that contain resin.