Calcineurin inhibitors play a critical role in dermatology by targeting immune responses, particularly in inflammatory skin conditions. Calcineurin itself is an enzyme within cells that drives certain processes in activated T-lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell involved in immune responses. When calcineurin inhibitors are used, they interfere with calcineurin by binding to cellular proteins known as immunophilins. This action results in the reduced release of the cytokine interleukin-2, a signaling protein, from T cells, which in turn slows down the proliferation of T cells. These effects make calcineurin inhibitors particularly useful in treating inflammatory skin diseases.
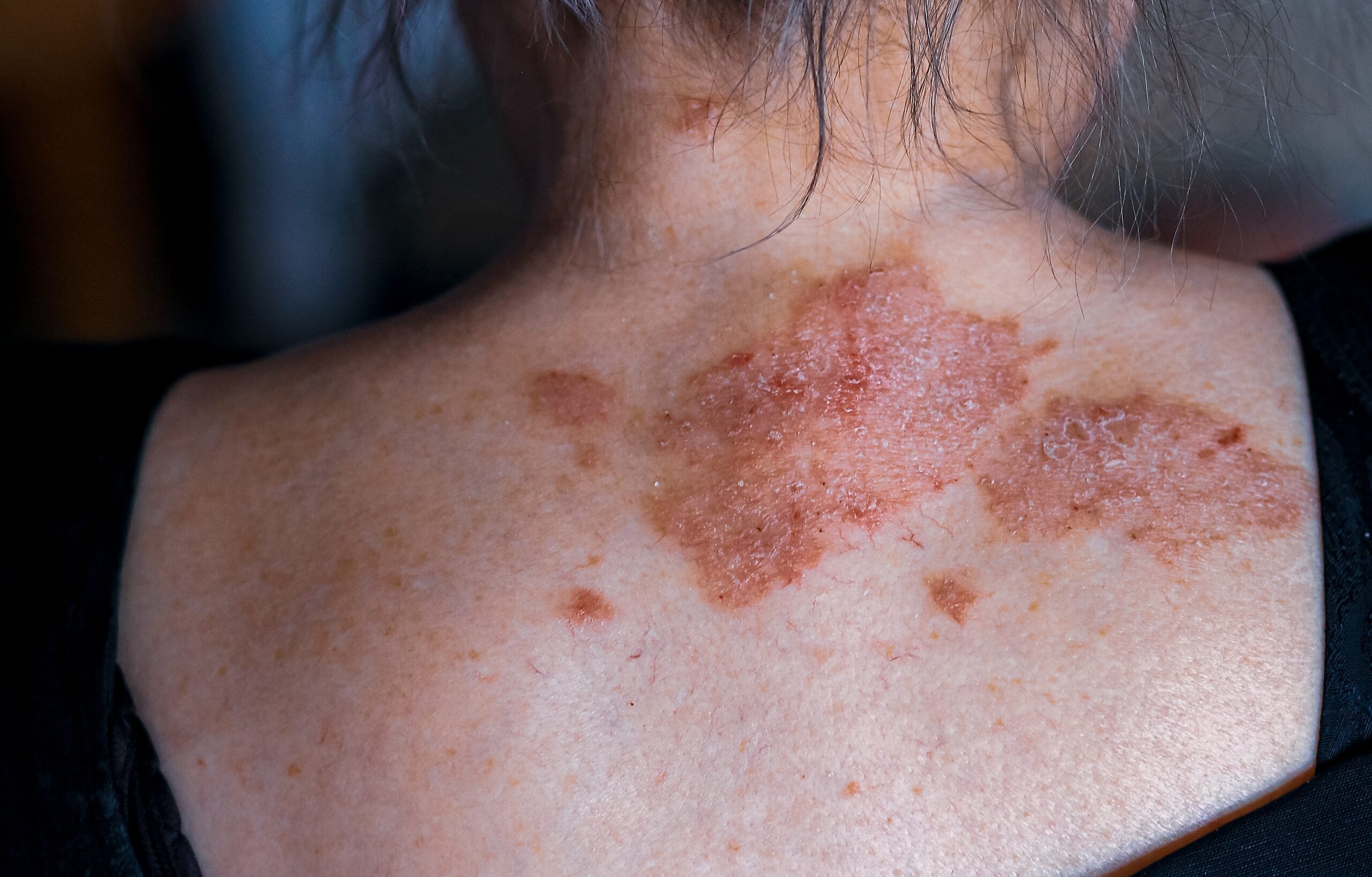
In dermatology, calcineurin inhibitors are utilized both topically and systemically to manage conditions such as atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. These drugs help to reduce inflammation and improve symptoms for patients dealing with chronic skin conditions.
Topical calcineurin inhibitors include pimecrolimus cream and tacrolimus ointment. Ciclosporin can also be used in topical form, although in some regions, it needs to be specially compounded. In addition to topical treatments, oral calcineurin inhibitors are available and include medications such as ciclosporin and tacrolimus, which are often used in more severe cases or when topical treatments are insufficient.
While calcineurin inhibitors can be highly effective, they are not without risks. One of the primary concerns with this class of drugs is their potential impact on kidney function, known as nephrotoxicity. This occurs because calcineurin inhibitors can increase endothelin-1, a substance that causes blood vessels to constrict, while reducing the levels of nitric oxide, which dilates blood vessels. They can also elevate transforming growth factor beta 1, which can contribute to tissue fibrosis in the kidneys.
To minimize these risks, healthcare providers aim to prescribe the lowest effective dose of calcineurin inhibitors and may combine them with other immunosuppressive medications that carry different risk profiles. This careful management helps balance the benefits of treating skin conditions with the need to protect overall kidney health.
In summary, calcineurin inhibitors are a valuable tool in dermatological treatments, particularly for inflammatory conditions like atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Their benefits, however, must be weighed against potential risks, especially concerning kidney function. Through careful dosing and, when necessary, combination therapy, dermatologists work to ensure safe and effective outcomes for their patients.