Centre for Medical and Surgical Dermatology
Board-Certified Dermatology for Complex Skin Conditions
Our Royal College-certified dermatology practice in Pickering provides comprehensive medical, surgical, and diagnostic care for complex skin conditions. Serving the Pickering, Durham and the Greater Toronto area with evidence-based dermatological treatments.








Our Specializations
Comprehensive Dermatological Care
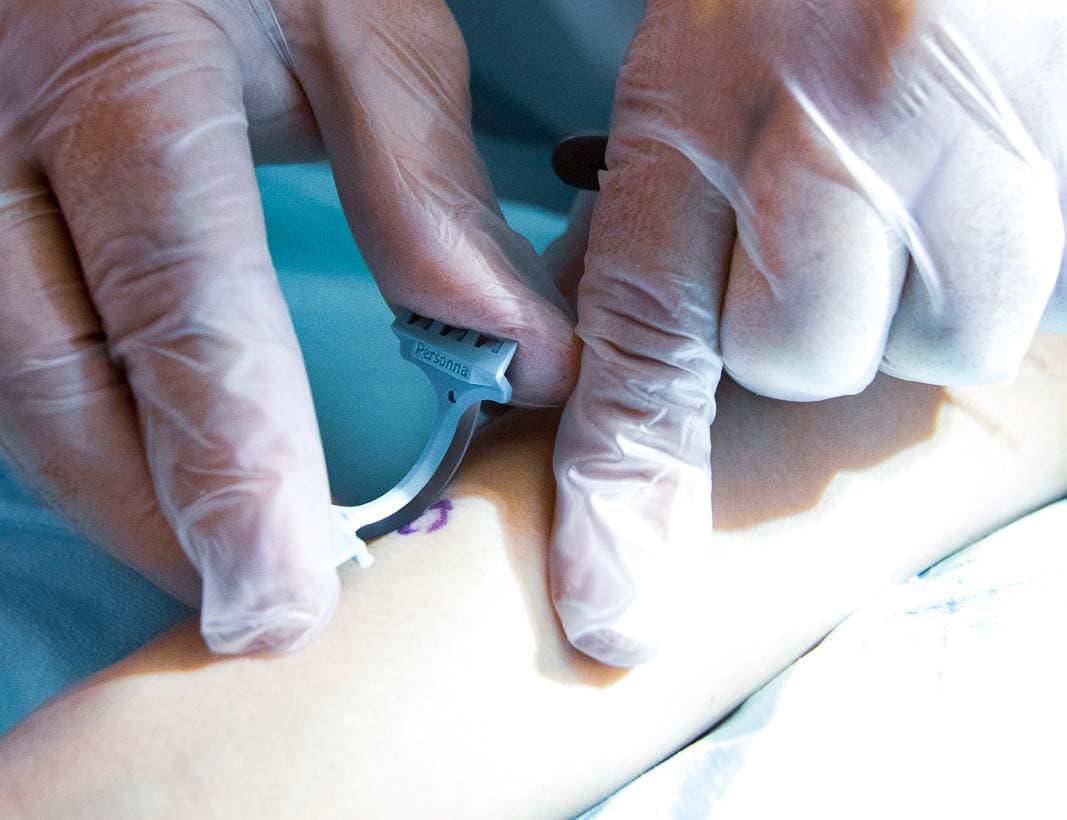
Medical Dermatology
Comprehensive treatment of complex medical skin conditions including severe psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, autoimmune disorders, and challenging skin diseases. All care provided under direct supervision of our board-certified dermatologist.
Surgical Dermatology
Advanced surgical procedures performed by our Royal College-certified dermatologist, including skin cancer excision, precision lesion removal, complex scar revision, and reconstructive dermatologic surgery.
About Surgical DermatologyDermato-Oncology
Specialized diagnosis and treatment of skin cancers by our board-certified dermatologist, including advanced diagnostic techniques, systematic monitoring, and coordinated multidisciplinary cancer care.
About Dermato-OncologyConditions We Treat
Focused on What Matters Most
Comprehensive care across the full spectrum of medical, surgical, and cosmetic dermatology conditions.

By the Numbers
Advancing Dermatological Care
Through expertise, innovation, and evidence-based practice.
25+
Years of Clinical Experience
8
Professional Affiliations
50,000+
Patients Treated
3,500+
Skin Cancer Cases Resolved
Your Dermatologist
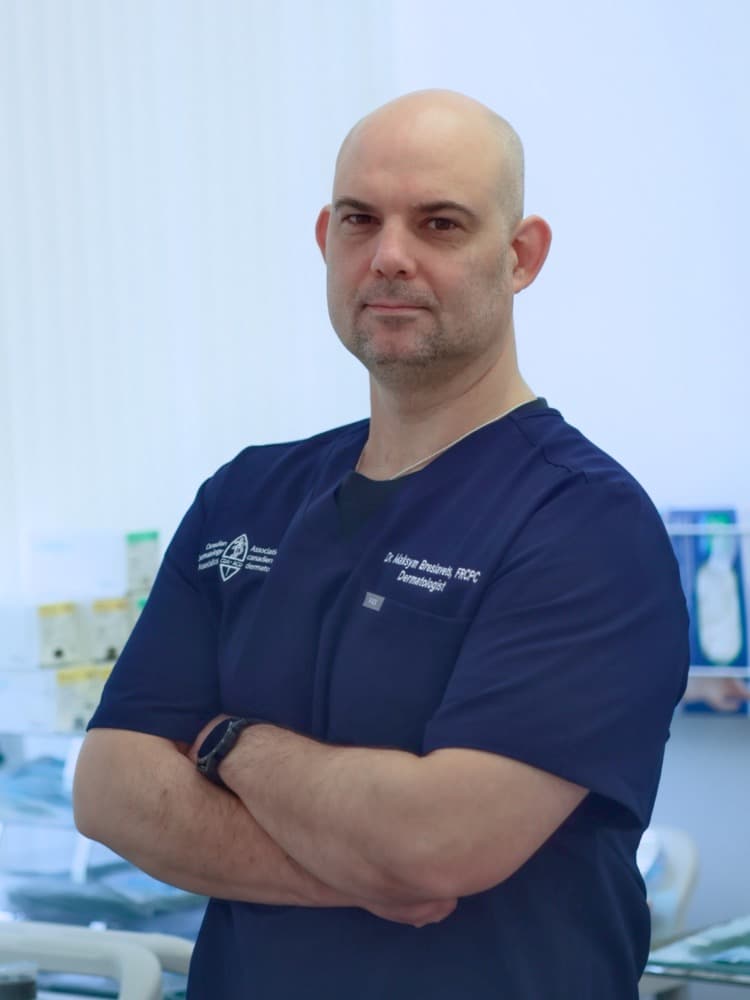
Dr. Maksym Breslavets
Led by Dr. Maksym Breslavets MD, PhD, FRCPC, a Royal College-certified dermatologist with international training and research experience. As a distinguished Fellow of the Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada, American Academy of Dermatology, and European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology, Dr. Breslavets brings extensive expertise in medical, surgical, and procedural dermatology, with a focus on evidence-based treatments, innovations and clinical research.









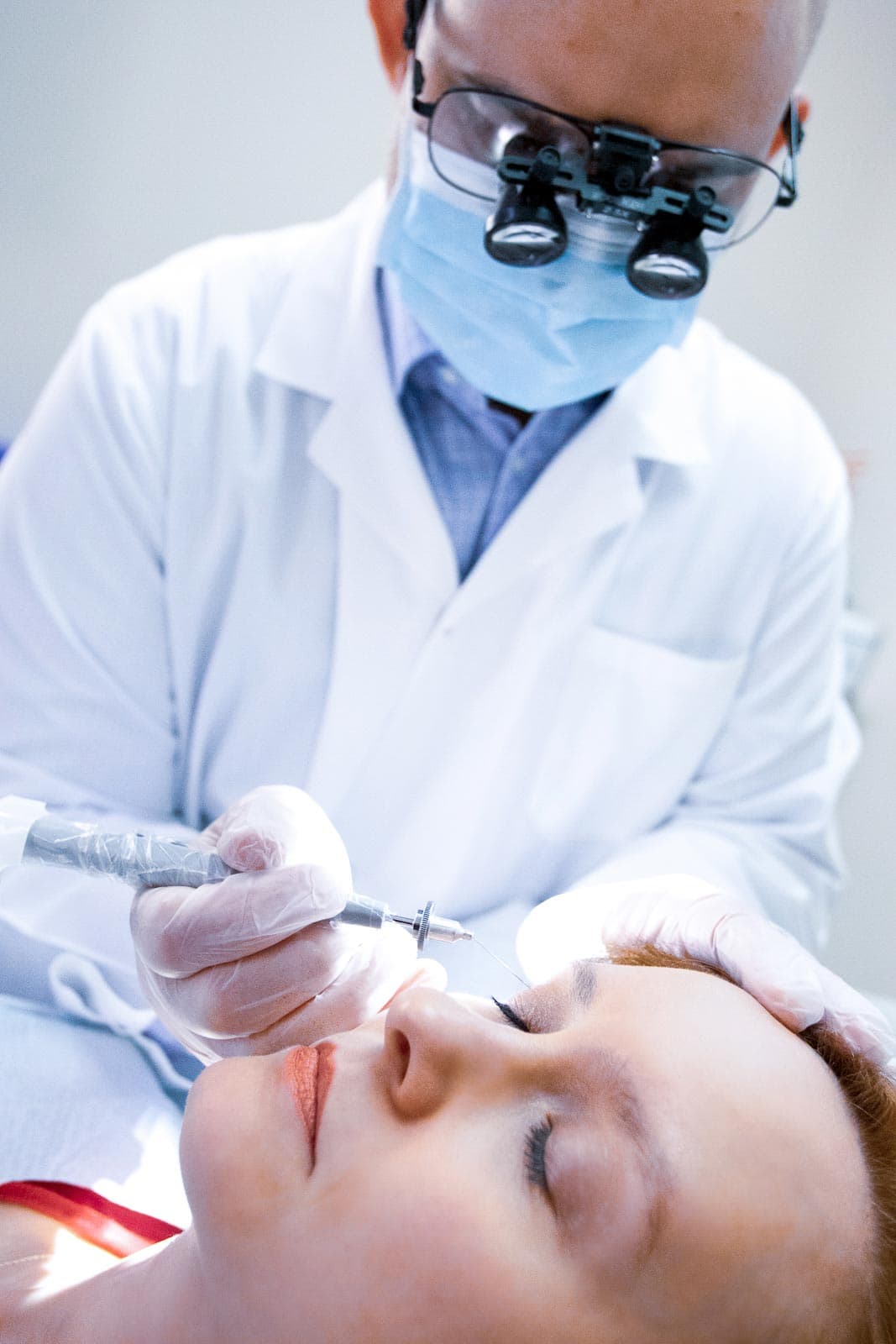
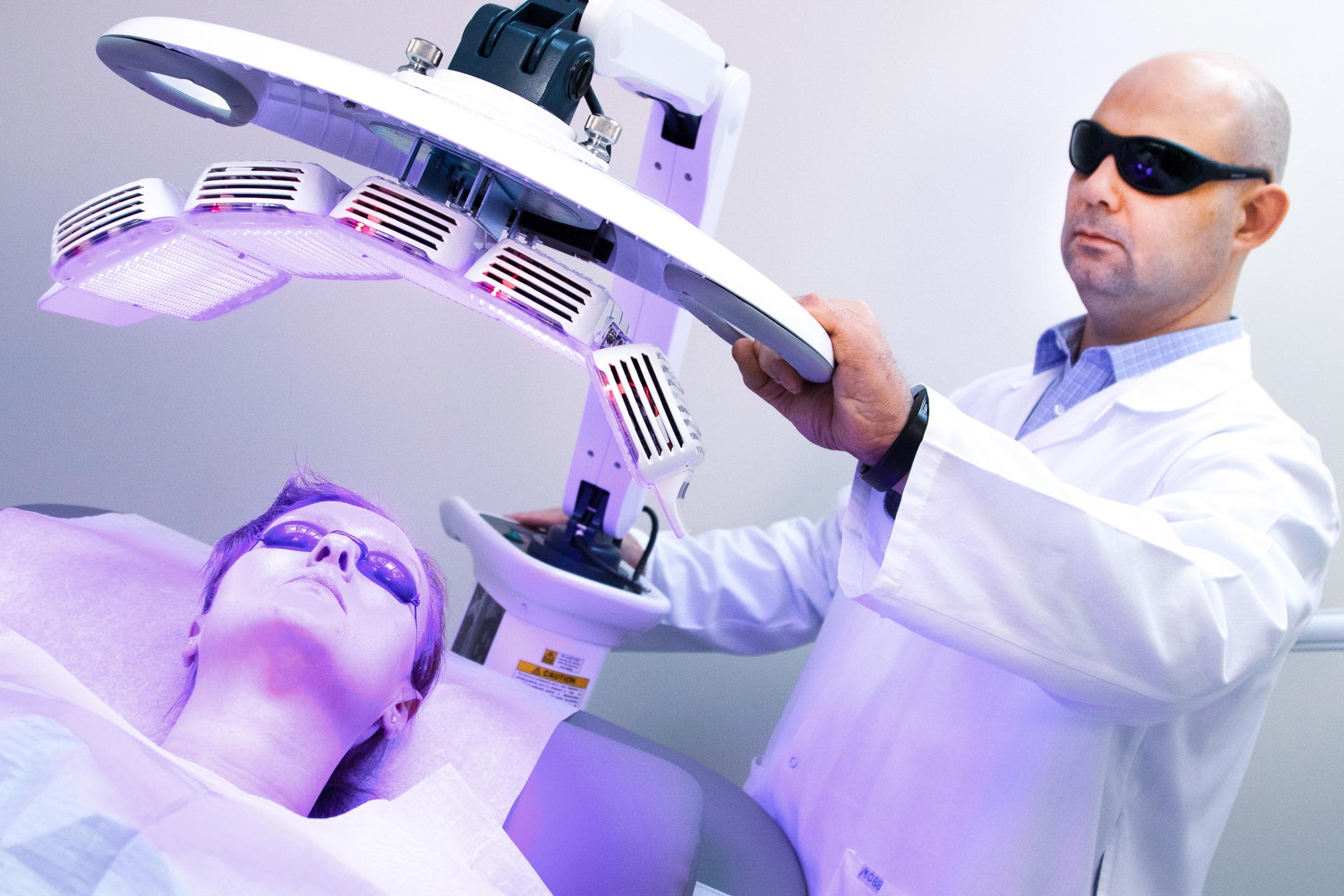
Procedural Dermatology
Advanced Skin Treatments
From microneedling and laser therapy to skin resurfacing and scar revision, Dr. Breslavets offers a range of procedures designed to rejuvenate and restore skin health. Each treatment plan is personalized, combining the latest techniques with clinical expertise to deliver effective, lasting results.
Why Choose CMSD
Why Choose CMSD
Proper medical diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions requires the expertise of a board-certified dermatologist for optimal patient outcomes. Our medical dermatology practice provides comprehensive physician consultation, diagnosis, and treatment for diseases of skin, hair and nails.
Board-Certified Expertise
Royal College-certified dermatologist with fellowships across North American and European academies, ensuring the highest standard of care.
Evidence-Based Care
Every diagnosis and treatment plan is grounded in the latest peer-reviewed research and clinical evidence for optimal patient outcomes.
Research-Driven Innovation
Active involvement in clinical research and AI applications in dermatology through the Skin e-Lab, bringing cutting-edge advances to patient care.
Comprehensive Treatment
Full spectrum of medical, surgical, and diagnostic dermatology services under one roof, from complex skin conditions to advanced procedures.
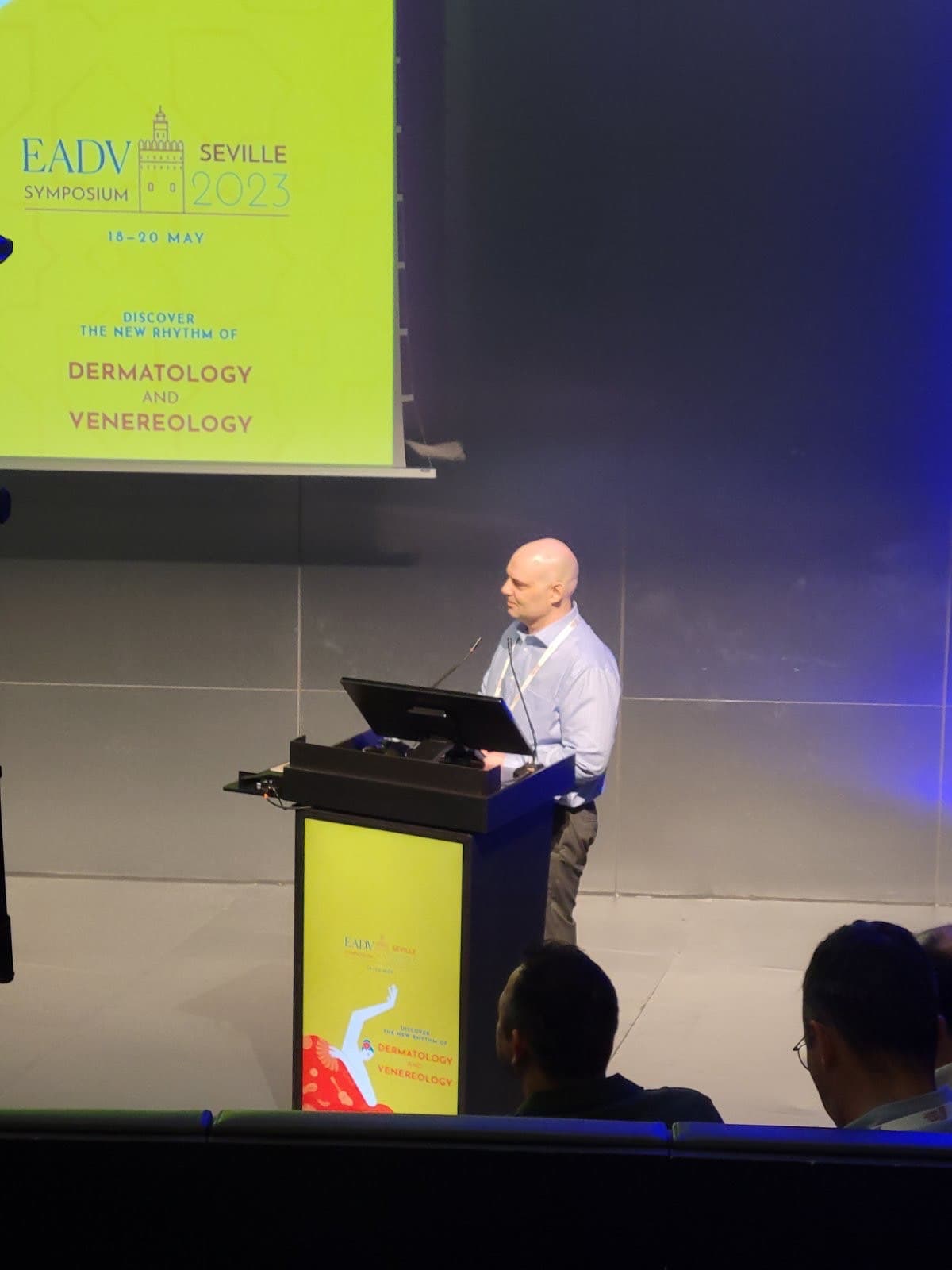

Advancing Dermatology Through Science
Every treatment recommendation at CMSD is grounded in the latest clinical evidence. Dr. Breslavets actively contributes to dermatology research, ensuring patients benefit from cutting-edge knowledge and proven therapeutic approaches.
International Leadership in Dermatology
Dr. Breslavets presents at leading international conferences and publishes in peer-reviewed journals, bringing global expertise and the latest advances directly to patient care in Ontario.

Getting Started
Your Path to Expert Care
Get a Referral
Request a referral from your family doctor or walk-in clinic. Your provider will fax it directly to our office.
Schedule Your Visit
Once the referral is received, the clinic will contact you to schedule an appointment at a convenient time.
Receive Expert Care
Meet with Dr. Breslavets for a thorough consultation, diagnosis, and personalized treatment plan.
Medical Dermatology
Comprehensive physician-directed care for complex skin conditions. Covered by provincial health insurance with a valid referral.
How to Book
Contact your family doctor or walk-in clinic to request a referral. Your provider will fax it directly to our office.
Procedural Dermatology
Professional elective removal of benign growths and advanced treatment options. No referral required.
- Board-certified dermatologist
- Advanced treatment techniques
- Convenient appointment times
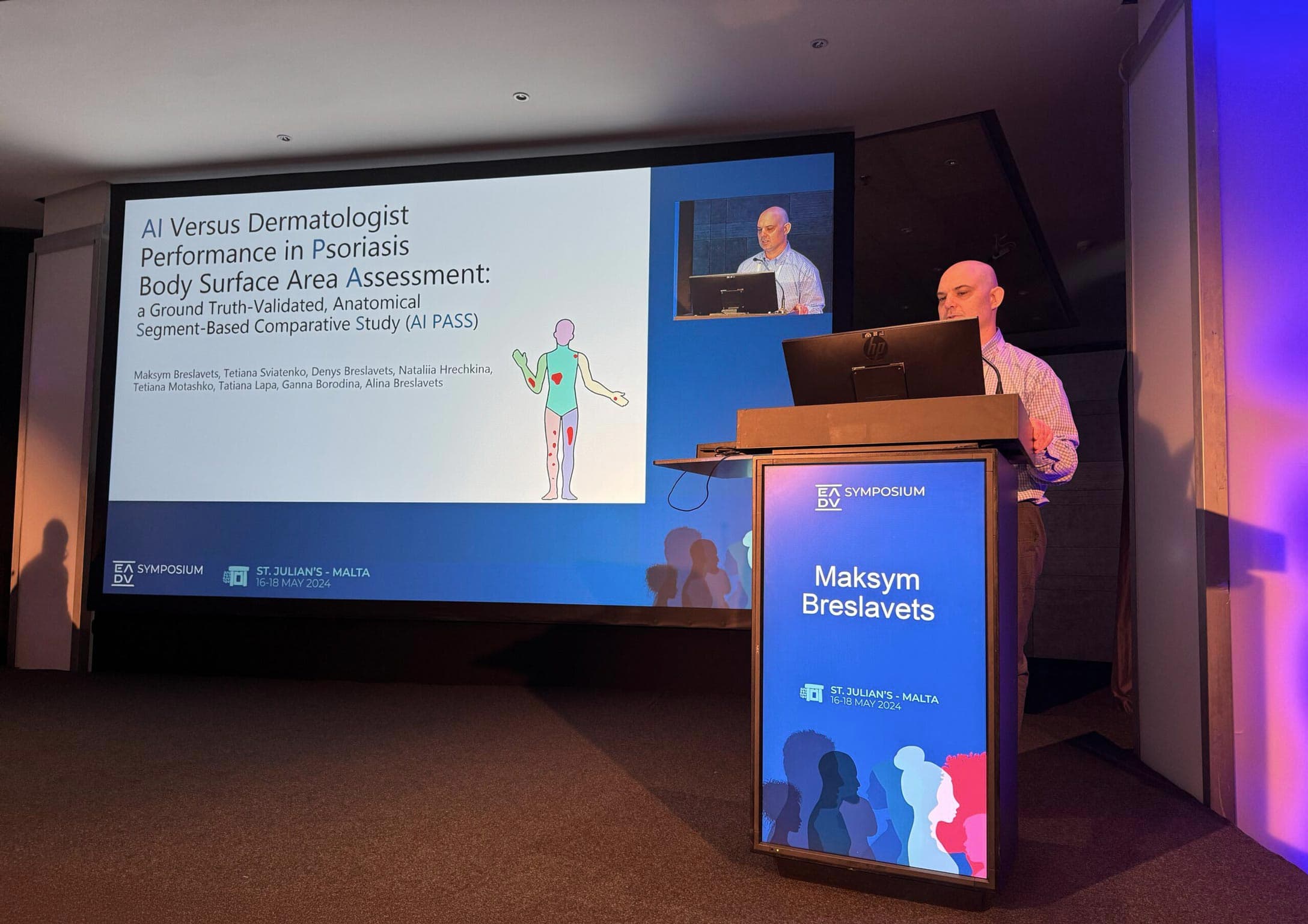

Research and Innovation
Excellence Through Innovation and Research
Our centre combines clinical excellence with academic research through our affiliated Skin e-Lab. Dr. Breslavets leads innovative studies in artificial intelligence applications for dermatology, contributing to peer-reviewed publications and international dermatology conferences.












Skin e-Lab
Groundbreaking research in AI applications for dermatology, bridging clinical care with technological innovation.
International Publications
Studies published in prestigious journals and presented at international dermatology symposiums worldwide.
Clinical Studies
Pioneering research in artificial intelligence applications in practical dermatology for improved patient outcomes.
Patient Reviews
What Patients Are Saying
Totally impressed with every aspect of my most recent appointment. I wish all health care in the province was this good.
March 1, 2026
Dr. Maksym Breslavets and his entire team are extremely professional, friendly, punctual, and courteous. I highly recommend them if you're in need of a dermatologist.
February 20, 2026
Punctual, very knowledgeable and provided effective treatment.
February 6, 2026
Always outstanding support from Doctor Breslavets and his staff. Very thorough in highlighting and fixing my skin damage.
January 23, 2026
Extremely efficient, both Doctor and staff! Well done.
November 21, 2025
I have been attending Dr. Breslavets for several years now. Always very professional and relatable.
October 25, 2025
It was a very good appointment. They work very hard and keep on top of everything. Thank you.
August 22, 2025
9 am appt on time! Seemed very knowledgeable and sympathetic to my issues. Very happy with this visit! Would recommend.
July 15, 2025
Expert!!! He found melanoma on my body and acted very quickly. It was removed very fast. Now he checks my body periodically to ensure no new cases found. Great professional.
May 2, 2025
Dr. Breslavets is very personable and thorough. He made sure I understood my condition, the ramifications and treatment plan. He quashed my fears by sharing his knowledge and kindness. His staff is welcoming - another level of comfort you, often, do not get at many specialist's offices. I feel safe going to Dr. Breslavets' office.
March 24, 2025
I was able to make an appointment quite quickly. I waited a very brief time in the office. Dr. Breslavets answered all of my questions, and did a very thorough examination. Very pleased with his professional service. Thank you.
January 30, 2025
It was professional and thorough. Already booked for next year. New building was easy to find and free parking.
November 23, 2024
Dr. Breslavets is a great dermatologist. I was referred to him in 2023. He was very thorough and was the one that discovered that I had malignant melanoma. His knowledge and efficiency were key to my case. And now as of 2024 I am cancer free thanks to him and Markham Stouville hospital. His staff are very personable and knowledgeable as well. I would recommend to anyone this is where you want to go.
September 25, 2024
Dr. Breslavets is extremely knowledgeable and efficient.
August 29, 2024
Doctor is very thorough and explains what he is doing in plain terms.
August 5, 2024
He was great! I had wished he had checked all over for anything suspicious instead I have to go a long way for another appointment.
July 17, 2024
Found the doctor to be very professional and thorough. I was seen at the appointed time which is a refreshing experience these days.
July 10, 2024
Excellent service on a follow up from a growth on my ear which is now healed. Will go back to see him in a year. Would definitely recommend Dr. Breslavets.
July 1, 2024
I appreciated the year follow-up to assess my progress after treatment. I expected that he would typically use nitro freezing on areas that need to be removed. It was a rather intense experience and quite painful and I had to take a strong Tylenol to get relief. I understand that sometimes this is necessary and not being critical. Dr. B had recommended in the past I use an exfoliating approved cream to remove dead skin which I had found very helpful. Perhaps I hadn't done it frequent enough as I was conscious that it also dried my scalp. Hope this feedback to Dr. B is helpful.
May 26, 2024
Poor communication in the waiting room as to what was expected next.
April 26, 2024
I have been seeing Dr. Breslavets since 2021 - he is incredibly knowledgeable and he is deeply caring about his patients. He managed to solve my long time issue that a few specialists couldn't. Great reception - very polite and always book a visit as soon as they have a referral. Thank you!
April 18, 2024
Drove 2 hours to see Dr. Breslavets and I was not disappointed at all. Great Dr, great staff. Will be back!!!
April 9, 2024
Excellent doctor. Thorough and knows exactly what needs to be done. Very confident in his abilities.
March 28, 2024
Professional, attentive, kind and thorough. I was very appreciative that even though he had a full waiting room he answered all of my questions.
February 28, 2024
Dr. Breslavets is a very professional and kind doctor. I have been his patient for a number of years and am very thankful for his medical expertise and thorough ongoing treatment of my skin cancer. His office staff are also excellent.
January 26, 2024
It turned out that the spots I had were of no concern. But Dr. Breslavets gave me some literature on what I had. The appointment was for 8:30 and I was in my car driving home before 9. Very punctual. Both the doctor and the front desk staff was very friendly. I was happy with the overall experience.
January 18, 2024
Dr. Breslavets is very thorough and is very good at finding any issues that may cause a problem for you. The staff is excellent and I have always been treated with great service.
December 14, 2023
Dr. Breslavets is an excellent Doctor. Very helpful and patient despite being so busy. He found my melanoma which I am grateful for. Not sure what would have happened if he didn't catch it. Thank you so much!
November 23, 2023
Prompt service. Good explanation of problem from doctor and immediate treatment.
November 11, 2023
He and staff are great! Highly recommended. Wait time was fast in waiting room plus the office. Thanks.
October 31, 2023
I have seen dr Breslavets on more than one occasion. He has always been very friendly and professional. I would definitely recommend him.
September 15, 2023
Dr. Breslavets and staff have been a pleasure to deal with!
July 25, 2023
Dr and staff were all great, on time and very helpful.
July 8, 2023
He has been terrific. He's been very effective in treating my issues.
June 22, 2023
Dr. Breslavets staff is exceptional. They are helpful and friendly. Dr. Breslavets is efficient, knowledgeable and explains procedures well.
June 2, 2023
Dr Breslavets and his colleagues are very helpful and have always made me feel comfortable and cared for.
May 16, 2023
Exactly on time, staff courteous and doctor very helpful and polite. Highly recommended!
May 3, 2023
Very professional and made me feel at ease. Felt very pleased with the results.
April 27, 2023
Extremely happy with what Dr. Breslavets did for me.
April 19, 2023
Friendly, willing to answer questions. Thanks so much.
April 9, 2023
Very happy. Short wait. Quick examination. Dr was very knowledgeable and explained everything well.
March 31, 2023
I have seen several Dermatologists over the last 35 years. I have been dealing with eczema and psoriasis for 35 years. I have try varies medications internal and external. I have even eliminate some foods to try and get some control on it. I felt embarrassed and developed low self-esteem. My first visit turned my life around. He recommended injections and set me up with a team of people involved with the medication and this summer I got to wear shorts and a bath suit. I cried, I was so happy.
March 23, 2023
Very professional. Makes you feel comfortable while being examined. Staff are helpful.
March 15, 2023
Prompt and professional care. I would definitely come back if required.
March 4, 2023
He took the time to explain and print out information for me to read.
February 9, 2023
In there and out in 10 minutes. That's how appointments are supposed to go - diagnosis, biopsy, treatment, follow up - all done professionally. He was great!
February 1, 2023
Dr. Breslavets is a fantastic dermatologist. His staff is also kind and helpful.
January 24, 2023
Dr. Breslavets and staff are always very nice and answer any question I ask. The appointment was right on time.
January 13, 2023
Excellent staff, amazing Doctor, great experience. Would definitely recommend.
January 5, 2023
Dr. Breslavets was very thorough and answered all of our questions in a very friendly manner. We were in and out in a good time. The girls were also very friendly and helpful.
December 29, 2022
Friendly staff and punctual. Professional and thorough. Would definitely recommend.
December 9, 2022
This was a quick efficient visit. I was very pleased with everyone's professionalism.
December 7, 2022
Wonderful, knowledgeable, professional, very kind and respectful Doctor. I'm 100 percent satisfied with my visit.
December 2, 2022
I have been visiting Dr. Breslavets for over 10 years. He is a true professional and very thorough. His staff has been very courteous and always prompt with answers regarding my appointments. I recommend Dr. Breslavets to anyone that needs any skin issues. Thank you.
November 25, 2022
I have been coming here for several years. The staff are professional and extremely knowledgeable. I highly recommend.
November 22, 2022
Returning patient. Dr. Breslavets is professional, knowledgeable and punctual.
November 21, 2022
Helpful, fast and efficient, feel in safe hands. I would definitely recommend them.
November 10, 2022
Good visit, only wish that someone had told me a hat band had stuck to my hair.
November 8, 2022
Great clinic! Dr. Breslavets is an amazing doctor!
October 16, 2022
Very thorough and easy to talk to. The staff are also helpful. Your appointment is on time which is a plus nowadays.
February 27, 2026
I have been seeing him for a few years now. He is so kind and helpful. He explains things properly and has great bedside manner. His girls at the desk are always nice as well!
February 20, 2026
Dr. Breslavets was very professional, attentive and knowledgeable. I saw him for sun damage and I am very satisfied with the care I received and grateful for a follow up appointment which many specialists do not provide. The clinic staff are focused on your needs and efficient with your time.
January 29, 2026
Dr. Breslavets is an exceptional doctor that always takes the time to answer all my questions. He never is in a rush to dismiss you. Staff are kind and knowledgeable. Always polite and ready to help. Five star all around.
January 23, 2026
The doctor was professional and answered my questions. Staff was great. Everything was well run.
November 21, 2025
I'm very pleased the way I was looked after. Very knowledgeable Doctor.
October 6, 2025
Above and beyond service. Absolutely outstanding in all areas. I had another question about another concern I had. My question was answered. I do know some people who have asked another question at doctor's appointment a specialist and a GP and they were dismissed. With a response of ... I don't have time for any other questions. I was very impressed that this was not the case. Everyone was so kind and helpful. I was as also impressed that I did not have to wait several months to receive my appointment. Thank you for such a pleasant experience.
August 15, 2025
Dr. Breslavets is a very knowledgeable, helpful, gentle and kind specialist. He is very thorough and an experienced dermatologist. He never rushes me through my appointments. He always answers my questions and provides me with follow up appointments. The staff is friendly and accommodating.
July 4, 2025
He checked my previous surgeries. But so quickly I didn't get a chance to ask about a new spot I noticed. Now I have until Feb to wait for him to check it.
May 1, 2025
Best dermatologist in town! Very knowledgeable, very empathetic to his patients. Dr. Breslavets goes beyond, helped me find the best suitable treatment for my chronic condition. His staff are very professional and kind.
March 4, 2025
Visit was great. Punctual, friendly and knowledgeable.
January 29, 2025
Had a worrying rough patch of skin that under home treatment would not go away. One visit and some chronic freezing a short scarring period and my patch was gone. Follow up was a short and quick.
November 19, 2024
Prompt, courteous service. Office staff are friendly.
September 13, 2024
An amazing, very knowledgeable, and kind specialist. I would recommend Dr. Breslavets. Staff is very kind and is very personable. 5 stars!
August 21, 2024
No long wait and Dr very professional and saves me drive to Toronto.
July 24, 2024
I have been seeing Dr. Breslavets for 4 years now for my autoimmune disease. He is very knowledgeable and very proactive. He is very thorough and leaves no stone unturned. I highly recommend him and his wonderful staff who are all kind, professional and very accommodating specially with regards to appointments.
July 13, 2024
Prior to my appointment I experienced a lot of anxiety related to my issue. The Doctor was very good at explaining that there was no reason for concern.
July 5, 2024
Great patient care and staff is very helpful. Thank you!
June 20, 2024
First visit was good and thorough. Very knowledgeable and friendly staff.
May 24, 2024
Excellent and personable. Very punctual, no waiting. New location is nice!
April 26, 2024
Dr B is incredible. Concise and caring. Being an outdoor person, I love knowing I can trust his diagnosis. Will be a patient on the new move as well.
April 12, 2024
I've always found Dr. Breslavets to be very professional and he has helped me with my skin problems.
April 4, 2024
The staff and Doctor Breslavets are very cordial and knowledgeable. I highly recommend this place for Dermatology.
March 18, 2024
Excellent treatment. Very thorough.
February 15, 2024
Really helpful, found time to see and manage a worrisome lesion promptly. This doctor and this office provide valuable services.
January 18, 2024
Efficient and respectful. Appointments unfold exactly as they indicate to you.
January 16, 2024
I can wear my glasses again! Dr Breslavets was able to gradually sort out several issues that I had on my face that were preventing me from wearing my glasses. He is the only Doctor that cared enough to help me with all these issues. The staff are very professional and are prompt to return phone calls.
November 30, 2023
Arrived at 11:45 am - went in to see Dr. And left the office at 12:15pm. Very efficient office.
November 17, 2023
Both staff and Dr B are great. They are well organized; punctual and pleasant. Dr B answers questions in a straightforward manner. Much appreciated. Thanks!
November 9, 2023
Dr. Breslavets is very knowledgeable, to the point, and always punctual. He has a wonderful staff to keep things moving quickly. 5 star!
October 29, 2023
Dr. Breslavets is very professional and straightforward when answering questions. Staff is approachable and efficient. I have been satisfied with 3 visits I had so far.
August 2, 2023
This is a knowledgeable doctor with great staff. The office is efficiently run and is respectful of patients time. I highly recommend this doctor.
July 14, 2023
Very professional, pleasant, staff are polite and knowledgeable.
July 5, 2023
Well-mannered. Confident. Eased my concern quickly. Straight to the point and informative.
June 7, 2023
Both Dr and staff were pleasant, felt very comfortable.
May 31, 2023
I was pleasantly surprised how quickly I got in to see the doctor.
May 4, 2023
On time and very efficient and pleasant staff. Dr seems very thorough although could explain findings a bit better.
April 28, 2023
Very punctual, knowledgeable, and helpful. Short wait time was appreciated as well.
April 24, 2023
Great staff, great doctors, great communication! Would be more ideal if parking was more convenient but aside from that everything to do with the doctor and the staff and the office was great. Thanks.
April 18, 2023
I saw Dr. Breslavets for a lesion on my back. He immediately knew what it was and offered to remove without charge. I highly recommend this dermatologist!
April 6, 2023
Dr. Maksym Breslavets was exceptional, I would highly recommend.
March 31, 2023
Dr. Breslavets is awesome. He is the best Derm I've seen. He is very knowledgeable. He listens and makes you feel very comfortable. Staff is great also.
March 22, 2023
Very thorough and kind. Staff are very efficient and I waited for a bit but the appointment was worth it. He did a full body check and I was really only scheduled for my eye. I was due for a full body. Thank you!
March 10, 2023
I was actually going to call them to thank them for their courtesy and promptness. He is a wonderful doctor and my appointment was perfect!
February 24, 2023
First appointment and Dr Breslavets put me right at ease. He answered all of my questions and I left feeling reassured. Staff was friendly, efficient and I was out quickly without feeling rushed. Excellent experience.
February 2, 2023
This office is very good and Dr Breslavets really knows his business. He has been right on with his diagnosis for my brother and I am also a patient of his and always states to come back if any more issues arise. Biopsies are done immediately after he looks at the problem you came in to see him about, if he thinks it might be cancer, no waiting.
January 28, 2023
Always professional, courteous, great staff - would recommend.
January 19, 2023
Courteous staff and thorough experience from the Doctor. Appointment was on time which was nice.
January 12, 2023
Everyone is very helpful and try to accommodate you.
December 29, 2022
This Doctor was professional, quick and friendly. He addressed several concerns and made me feel at ease. Thank you for a great experience.
December 19, 2022
Good staff and punctual. Addressed all my needs in a timely manner.
December 9, 2022
Quick, efficient and friendly. Treatment was explained.
December 6, 2022
Professional, thorough, easy to get an appointment and follow up. I would recommend him.
December 1, 2022
Service was prompt, matter of fact. I had confidence in the doctor and the outcome of his suggestions.
November 24, 2022
Dr. Breslavets is a brilliant and respectable Dermatologist. His staff, everyone at the clinic, are wonderful. If it wasn't for Dr. Breslavets and his team I don't know where my skin condition would be. I have been a patient of Dr. Breslavets and his team for well over 2 years now and my skin condition is remarkable and relieved. Nothing but good things to say here.
November 22, 2022
Very punctual. He is very helpful and staff are pleasant.
November 18, 2022
I had a problem with very itchy skin around my nose, my doctor suspected cancer. To my relief it was Dermatitis. Dr. Maksym made me aware of that and gave me some cream to relieve it. Thank you.
November 10, 2022
This was a very punctual and efficient visit. Thanks.
November 2, 2022
Very efficient and a good communicator. I believe he is right on top of keeping my skin healthy!
February 27, 2026
Dr. B is always helpful and clear with the treatment plan. Always a positive experience.
February 13, 2026
He was sincere to my questions and very helpful. He was also proactive and checked other areas to make sure all was good (which it was). I'd recommend him for sure!
January 24, 2026
I have found Dr. Breslavets to be an exceptional dermatologist. He performed a delicate procedure that I needed with great skill and precision. Thank you Dr. Breslavets!
December 10, 2025
I have been his patient for the past four years. Dr. Breslavets has always been very thorough in his examinations and professional. The staff are very helpful and accommodating.
October 30, 2025
Dr. Breslavets and his team are well organized and work efficiently in a positive environment. Dr. Breslavets is extremely knowledgeable and efficient.
August 28, 2025
Excellent medical service, thorough and efficient, answered all my questions with care and consideration. Staff was kind and professional.
July 15, 2025
Dr Breslavets has always been there for me. An expert in his field of dermatology. I travel a few hours distance to see him. Appointments are scheduled yearly, and never have to wait to see him. His staff are courteous.
June 6, 2025
Totally professional and pleasing staff! Waiting time was minimal!
March 24, 2025
No complaints concerning Dr. Breslavets and staff. I also found my visits to be punctual, the staff friendly and Dr Breslavets knowledgeable and more than happy to answer any questions or concerns I may have.
February 19, 2025
Very professional and caring! I have been going for approximately 3 years.
December 14, 2024
I have been seeing this clinic for two years now and I have never had an issue.
November 14, 2024
I am very happy with the Dr.'s suggestion to change the type of medication I was previously on. The results have been extremely positive.
September 4, 2024
Very professional and well organized. Excellent communication and follow up. Also, very personable caring. Great team and very glad I'm in their care.
August 10, 2024
I had suffered with a skin condition for 20 years. He prescribed the right medication and my skin is clearing up fabulously. So thankful for his knowledge.
July 23, 2024
Dr. Breslavets and his staff are amazing. Friendly, thorough, takes time to answer questions instead of rushing off to his next patient.
July 11, 2024
All went very well. On time and very polite and virtuous. Clean office. Easy to get to location. Great parking.
July 1, 2024
Yearly check up. As usual everyone was helpful, polite and professional.
June 4, 2024
The staff was very friendly and helpful, my appointment was on time and the doctor was very nice and met all my needs.
May 24, 2024
Terrific doctor. Pays attention to your problems. Very attentive.
April 20, 2024
Great doctor and staff. Very gentle and caring. Have recommended to several people.
April 12, 2024
Excellent care, takes the time to examine and provide thorough treatment.
March 29, 2024
Very pleased with the treatment I received. Dr Breslavets is awesome. He listens and answers questions. Amazing Doc!!!
March 12, 2024
Always a good experience. Prompt and knowledgeable service.
February 14, 2024
Dr. Breslavets is an excellent dermatologist. He is very knowledgeable, helped me with my skin issues and took time with me. I am very grateful. The staff is very respectful, polite, and kind. They always treat me with respect. Thank you Dr. Breslavets and your staff.
January 18, 2024
Very efficient and friendly staff with a great Doctor. What more could you ask for.
January 12, 2024
Dr. Breslavets and staff were prompt, polite and thorough, each time I have visited their office.
November 28, 2023
I appreciate the time spent seeing me. I always receive professional service and my questions and concerns are always taken seriously.
November 14, 2023
Punctual for a specialist office. Very helpful staff. The Dr and his assistants are always pleasant to deal with.
November 9, 2023
Super efficient staff, very friendly and supportive.
September 29, 2023
Dr. Breslavets was professional, knowledgeable and reassuring. Staff were very efficient.
July 26, 2023
Very thorough and pleasant. Right to the point when answering inquiries.
July 8, 2023
Very professional and good at educating me on the subject.
June 28, 2023
Good location, nice staff and office. Dr. Breslavets is efficient.
June 2, 2023
Very personable and staff very pleasant. Made me feel comfortable.
May 26, 2023
I was very pleased with the results of my appointment. Thank you.
May 4, 2023
Wait time is minimal compared to other dermatologists I have seen. Dr. Breslavets saw a mark on my upper arm as I was leaving! (I didn't even notice it). The spot had pre cancerous cells. He is very kind. Staff are very pleasant.
April 27, 2023
I am very happy with this doctor and office staff.
April 21, 2023
I had an excellent experience! Staff was lovely and friendly! The doctor was wonderful.
April 14, 2023
My experience with Dr. Breslavets has always been exceptional. This visit was a last minute request for me and his staff arranged an appointment in a very timely manner. I would highly recommend Dr Breslavets and his staff.
March 31, 2023
The staff were friendly. Dr. Breslavets is very knowledgeable, kind and was able to let me know immediately what my skin problem was. I would highly recommend!
March 29, 2023
Pleasant staff. Dr is very knowledgeable and makes me feel comfortable and confident about the care I have been receiving.
March 17, 2023
I find Dr. Breslavets very thorough on my yearly visit. Staff are friendly and pleasant.
March 9, 2023
Provided me realistic expectations of my ailment and available treatments. Made me heard and understood and was punctual and professional at all times. The staff was great and polite. I would recommend Dr. Breslavets and his clinic to anyone who needs dermatological help.
February 13, 2023
Overall a very good experience and very professional doctor and staff.
February 1, 2023
Dr. Breslavets was very resourceful in helping me navigate my eczema challenges.
January 24, 2023
Very professional. I appreciated his knowledge and thoroughness.
January 18, 2023
Dr. was very professional. Secretary was helpful.
January 11, 2023
Very professional Doctor... very professional staff.
December 29, 2022
They are very professional and the clinic is always nice and neat. I highly recommend Dr. Maksym Breslavets.
December 14, 2022
A Friendly and knowledgeable Dr. Staff very nice!
December 9, 2022
Very pleased with punctuality, polite and professional. Would definitely revisit.
December 2, 2022
Professional, thorough, knowledgeable. Recommend asking for Dr. Breslavets if a referral for a dermatologist is required.
December 1, 2022
Very thorough and professional. Easy to talk through any questions.
November 23, 2022
The doctor and staff are always pleasant and informative. I'm very happy with this clinic.
November 22, 2022
Extremely friendly and professional staff. My appointment was on time and the doctor was as always professional, friendly and attentive.
November 11, 2022
Very helpful, pleasant, knowledgeable. I would recommend this doctor and his team.
November 8, 2022
Excellent. Efficient. No wait time. Great staff.
October 31, 2022
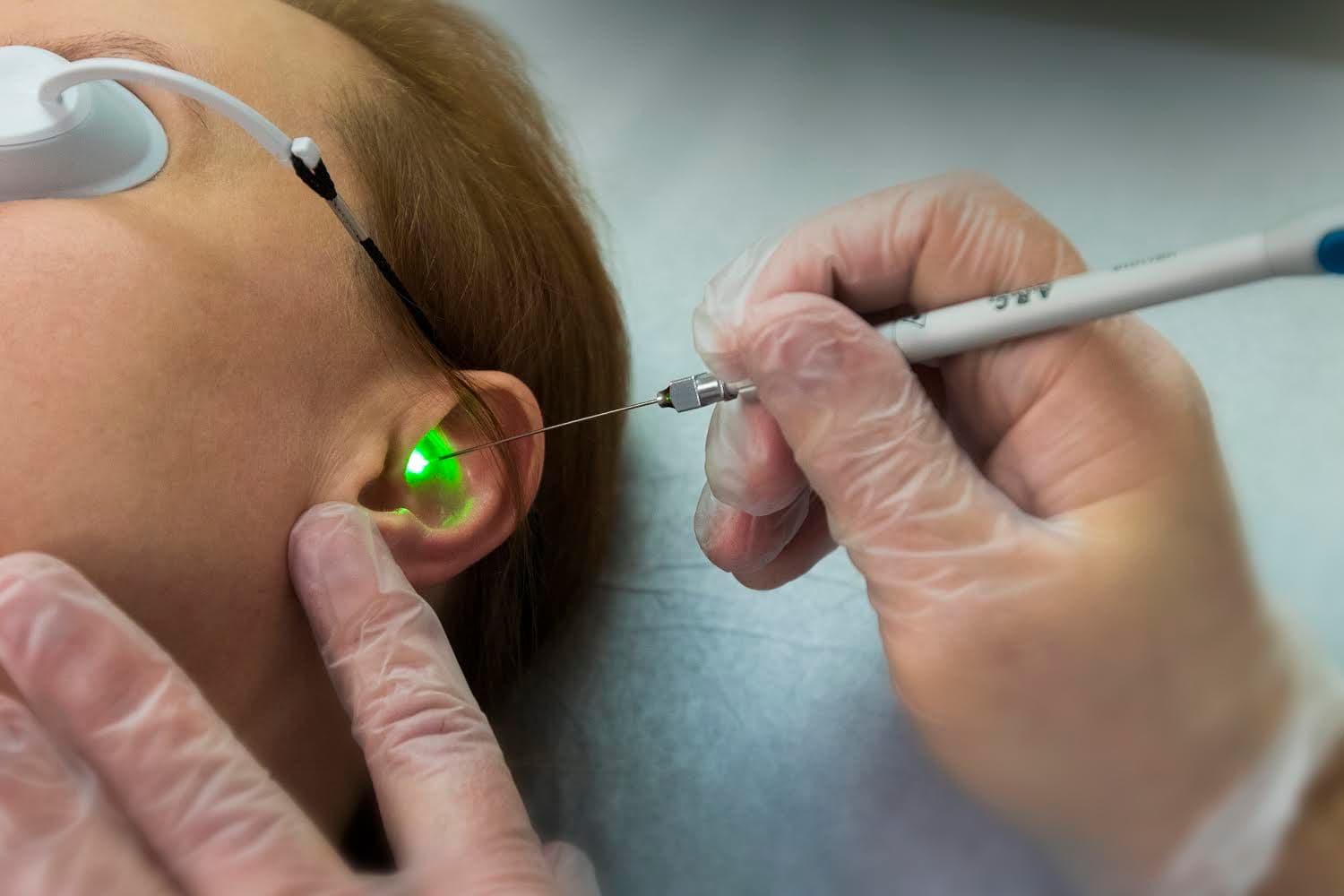
Procedural Dermatology
Growth and Lesion Removal
Unwanted moles, skin tags, cysts, vascular lesions, and other growths can be safely and precisely removed with minimal scarring. Dr. Breslavets evaluates each case individually, selecting the most appropriate technique to ensure optimal cosmetic outcomes and patient comfort.
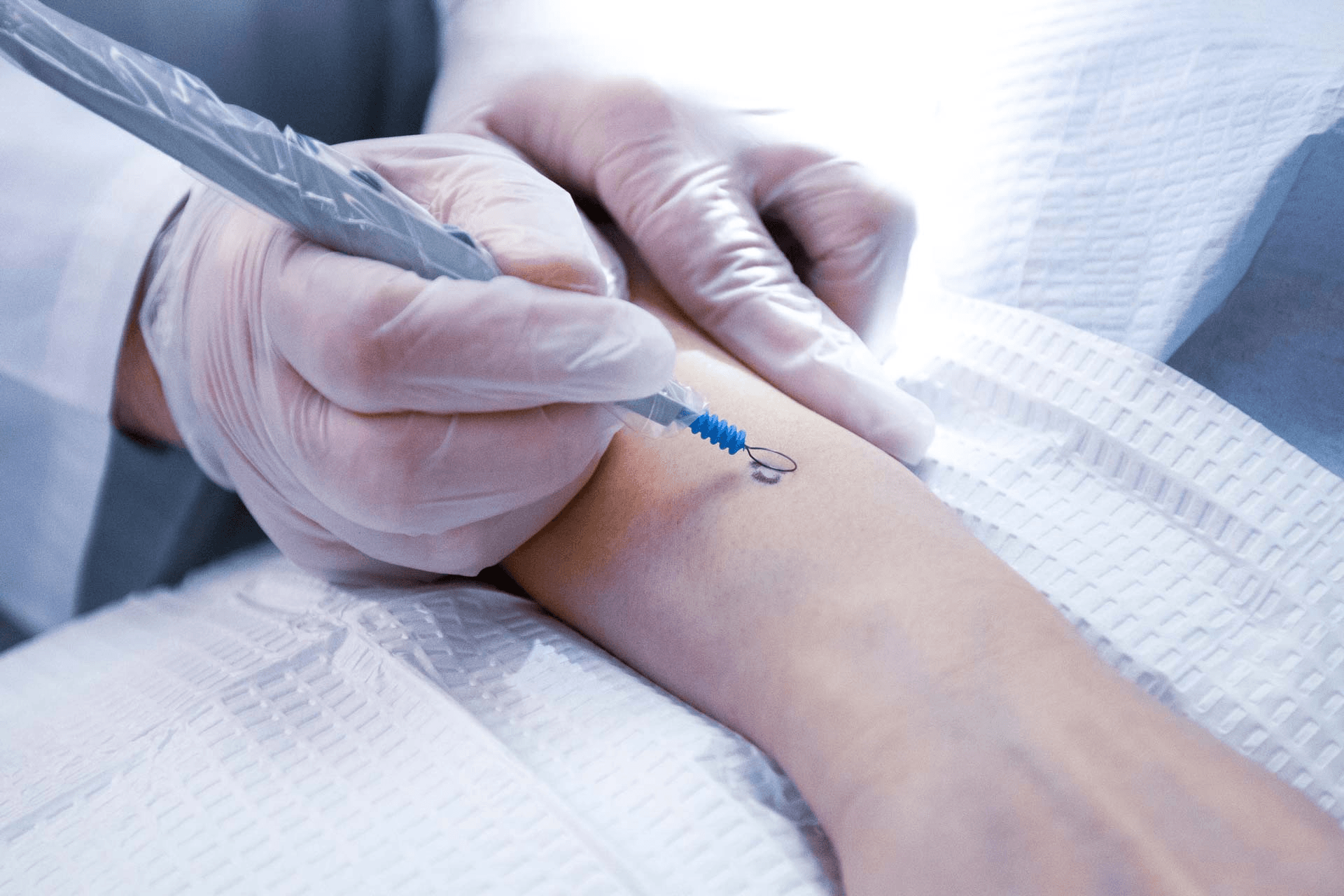
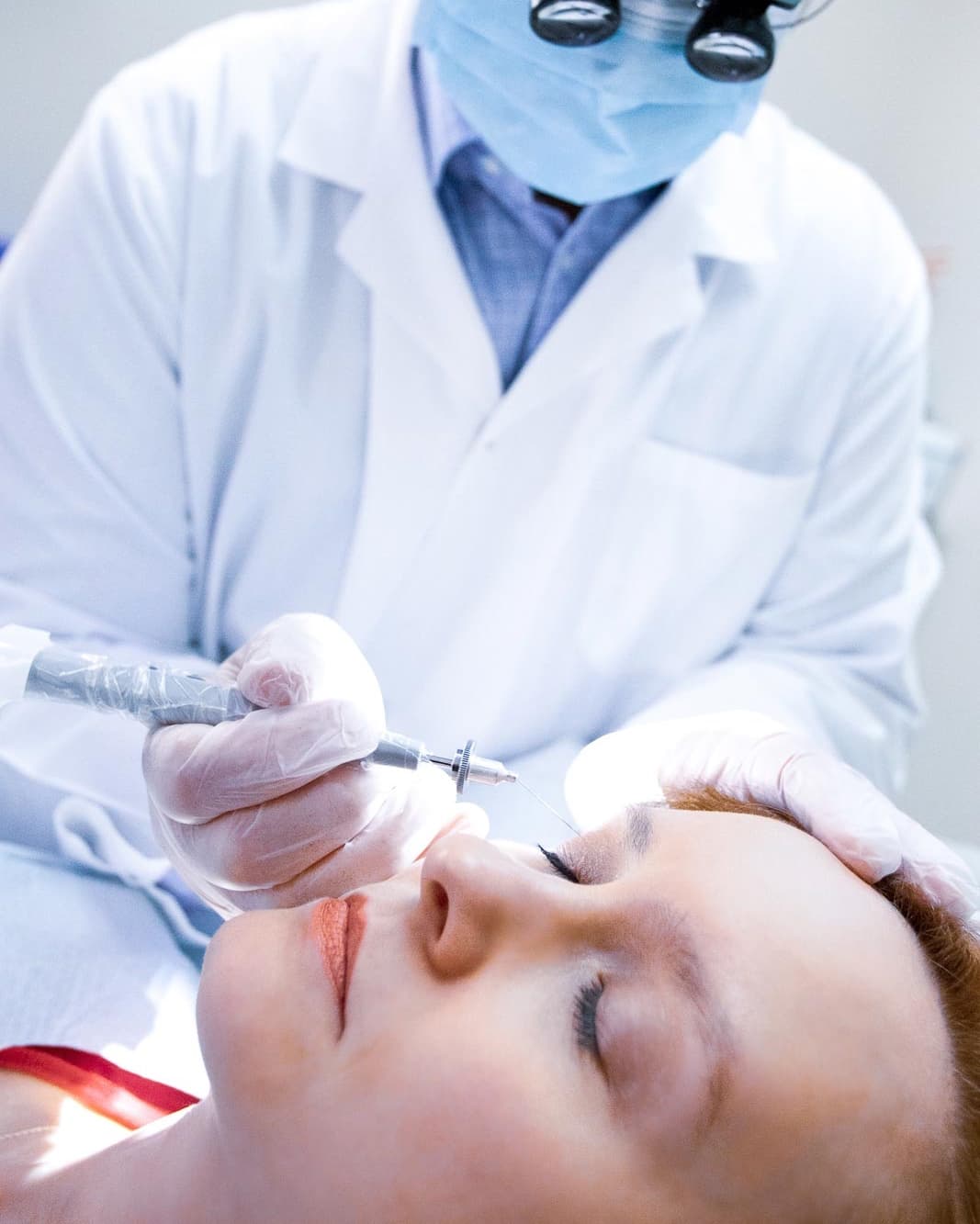
Procedural Dermatology
Book a Consultation
Procedural dermatology services are available without a physician referral. Complete the form below to request a consultation for growth removal, laser treatments, or other procedures.
From the Clinic
Dermatology Insights and Resources
Our expert team regularly shares valuable information about skin conditions, treatment advances, and practical skincare advice.
Common Questions
Frequently Asked Questions

Have questions about visiting the clinic or booking a procedure? Below are some common inquiries. For the complete list, visit the FAQs page or contact the clinic directly.
The following items should be brought to the first appointment:
- A valid Ontario health card
- A list of current medications and supplements
- Medical history and any previous dermatology records
- Photos of the skin condition if it comes and goes
- A list of questions for the dermatologist
Ready to Take the Next Step?
Whether you need a physician referral for medical dermatology or would like to book a procedural consultation directly, our clinic is ready to provide expert dermatological care.
Or call us directly at (905) 493-5700