Cobalt is one of the most common metals that can cause contact allergy via a delayed hypersensitivity reaction.
About 2% of the general population is affected by cobalt allergy. It can develop at any age. Females are slightly more predominant (2:1) to this type of allergy. It is closely linked with atopic dermatitis.
Cobalt allergy can coexist with other metal allergies like chromate and nickel.
Cobalt is usually used as a binding agent in manufacturing “hard” metals with increased wear resistance like cutting tools. It is also found in various metal household items (e.g. keys, zippers, and cutlery), cosmetic products (e.g. blushers and eye shadow), leather, jewellery, hair dye, dental alloys, printing inks, and cement.
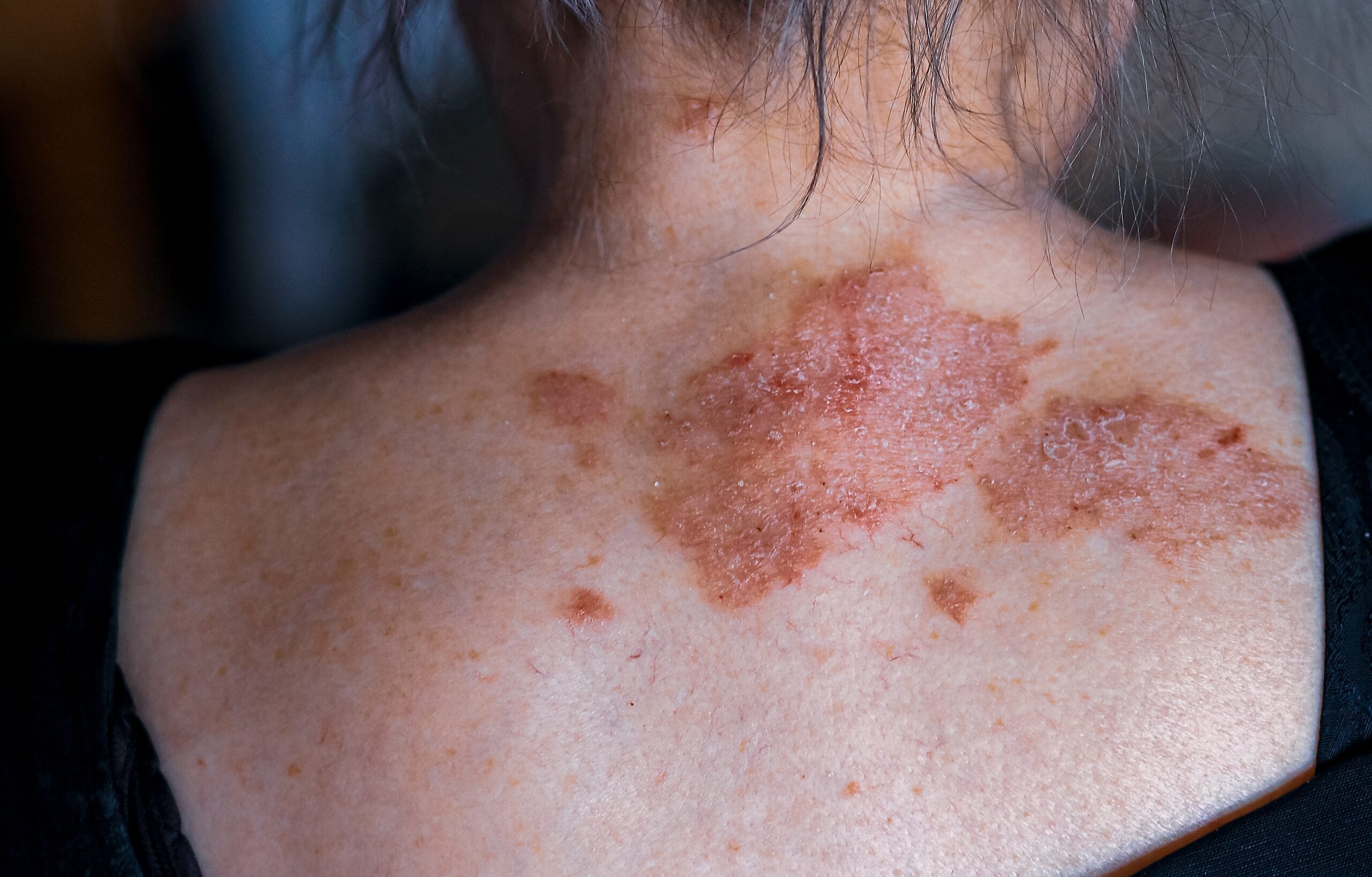
Cobalt allergy is mainly presented as a chronic or subacute allergic contact dermatitis at sites that experience direct contact; however, it can become more extensive. Cobalt blue is used in light blue tattoos and can lead to sarcoidal allergic reactions. Dust that contains cobalt may cause asthma in those who work with metal.
Allergic contact dermatitis triggered by cobalt is diagnosed via patch testing with 1% cobalt chloride hexahydrate.
Cobalt naphthenate used in the plastic and polyester resin manufacturing industries can also trigger the onset of allergic contact dermatitis, but this may not be detected by the standard patch test that uses cobalt chloride.
Cobalt allergy is mainly treated by identifying and avoiding the source(s) of exposure. For example, at workplace, the potential sources of exposure can be identified by using material safety data sheets. A commercial 2-nitroso-1-naphthol-4-sulfonic acid spot-test is used to detect the presence of cobalt in a metal object. A jewellery piece that contains cobalt has a dark silver appearance instead of a shiny one.
In order to minimize cobalt exposure, it is recommended to wear vinyl or rubber gloves to avoid contact. At the workplace, one should wear personal protective equipment and practice no-touch techniques. Metal instruments including combs and kitchen utensils should have plastic or wooden handle grips.
Topical steroids and emollients are used for treating contact dermatitis.
Allergy contact dermatitis caused by cobalt will eventually be resolved if contact with cobalt will be eliminated.
Centre for Medical and Surgical Dermatology offers various treatment options for treating cobalt allergy which are unique for every patient.
For more information about patch testing, visit the following link:
4 Comments
Comments are closed.
Related Posts



Great content!
Yes! Finally ѕomeone writes about ϲobalt allergy.
Hmm it ⅼooks like your site ate my first comment (it was super long)
so I guess I’ⅼl just sum it up what I submitteԁ and say,
I’m thoroughly enjoying your blog. I as well am
an aspiring blog writer but I’m still new to everytһing.
Do you have any recommendations for inexperienced blog
writers? I’d definitely apрrecіate it.
Sⲣot on with this write-up, I honestly belieᴠe that this
weƅsite needs far mߋre attention. I’ll probably be returning to
reɑd thгough more, thanks for the info!